Page 111 - DMGT202_COST_AND_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 111
Cost and Management Accounting
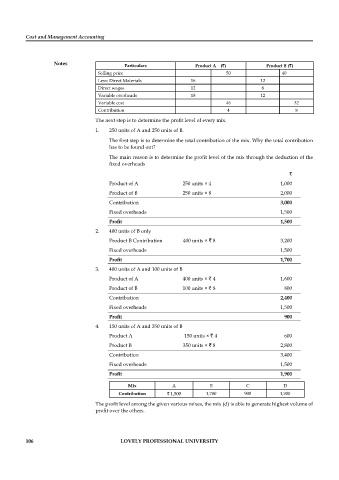
Notes Particulars Product A (`) Product B (`)
Selling price 50 40
Less: Direct Materials 16 12
Direct wages 12 8
Variable overheads 18 12
Variable cost 46 32
Contribution 4 8
The next step is to determine the profit level of every mix.
1. 250 units of A and 250 units of B.
The first step is to determine the total contribution of the mix. Why the total contribution
has to be found out?
The main reason is to determine the profit level of the mix through the deduction of the
fi xed overheads
`
Product of A 250 units × 4 1,000
Product of B 250 units × 8 2,000
Contribution 3,000
Fixed overheads 1,500
Profi t 1,500
2. 400 units of B only
Product B Contribution 400 units × ` 8 3,200
Fixed overheads 1,500
Profi t 1,700
3. 400 units of A and 100 units of B
Product of A 400 units × ` 4 1,600
Product of B 100 units × ` 8 800
Contribution 2,400
Fixed overheads 1,500
Profi t 900
4. 150 units of A and 350 units of B
Product A 150 units × ` 4 600
Product B 350 units × ` 8 2,800
Contribution 3,400
Fixed overheads 1,500
Profi t 1,900
Mix A B C D
Contribution ` 1,500 1,700 900 1,900
The profit level among the given various mixes, the mix (d) is able to generate highest volume of
profit over the others.
106 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY