Page 162 - DMGT202_COST_AND_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 162
Unit 8: Budgetary Control
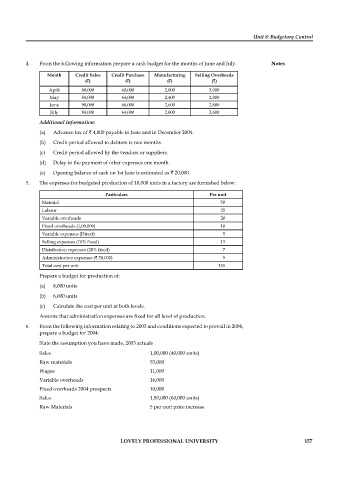
4. From the following information prepare a cash budget for the months of June and July. Notes
Month Credit Sales Credit Purchase Manufacturing Selling Overheads
(`) (`) (`) (`)
April 80,000 60,000 2,000 3,000
May 84,000 64,000 2,400 2,800
June 90,000 66,000 2,600 2,800
July 84,000 64,000 2,000 2,600
Additional Information:
(a) Advance tax of ` 4,000 payable in June and in December 2004.
(b) Credit period allowed to debtors is two months.
(c) Credit period allowed by the vendors or suppliers.
(d) Delay in the payment of other expenses one month.
(e) Opening balance of cash on 1st June is estimated as ` 20,000.
5. The expenses for budgeted production of 10,000 units in a factory are furnished below:
Particulars Per unit
Material 70
Labour 25
Variable overheads 20
Fixed overheads (1,00,000) 10
Variable expenses (Direct) 5
Selling expenses (10% fi xed) 13
Distribution expenses (20% fi xed) 7
Administration expenses (` 50,000) 5
Total cost per unit 155
Prepare a budget for production of:
(a) 8,000 units
(b) 6,000 units
(c) Calculate the cost per unit at both levels.
Assume that administration expenses are fixed for all level of production.
6. From the following information relating to 2003 and conditions expected to prevail in 2004,
prepare a budget for 2004:
State the assumption you have made, 2003 actuals
Sales 1,00,000 (40,000 units)
Raw materials 53,000
Wages 11,000
Variable overheads 16,000
Fixed overheads 2004 prospects 10,000
Sales 1,50,000 (60,000 units)
Raw Materials 5 per cent price increase
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 157