Page 194 - DMGT202_COST_AND_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 194
Unit 11: Ratio Analysis
! Notes
Caution Standard norm of the current ratio:
The ideal norm is 2:1; which means that every one rupee of current liability is appropriately
covered by two rupees of current assets.
High ratio leads to greater the volume of current assets more than the specified norm denotes
that the firm possesses excessive current assets than the requirement portrays idle funds invested
in the current assets.
A big limitation of current ratio is that under this ratio, the current assets are equally weighed
against each other to match the current liabilities. One rupee of cash is equally weighed at par with
the one rupee of closing stock, but the closing stock and prepaid expenses cannot be immediately
realized like cash and marketable securities.
11.3.2 Acid Test Ratio
It is a ratio expresses the relationship in between the quick assets and current liabilities. This ratio
is to replace the bottleneck associated with the current ratio. It considers only the liquid assets
which can be easily translated into cash to meet out the fi nancial commitments.
Liquid Assets
Acid Test Ratio (Quick Assets Ratio) =
Current Liabilities
Liquid Asset = Current Assets – (Closing Stock + Prepaid Expenses)
Example: A company has a closing stock of ` 30,000 while its prepaid expenses are
` 5000. What will be its quick assets ratio if the current assets are worth ` 50000 while current
liabilities are worth ` 15000?
Solution:
Liquid Asset = Current Assets – (Closing Stock + Prepaid Expenses)
= 50000 – (30000 + 5000)
= 15000
Liquid Assets
Quick Assets Ratio =
Current Liabilities
= 15000/15000 = 1:1
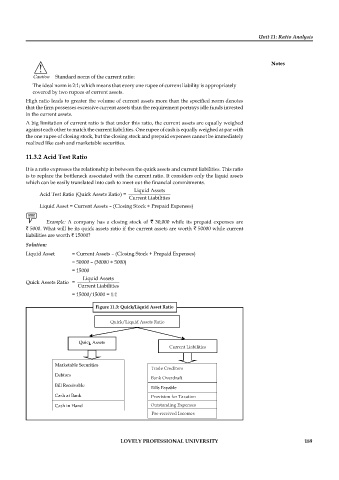
Figure 11.3: Quick/Liquid Asset Ratio
Quick/Liquid Assets Ratio
Current Liabilities
Trade Creditors
Bank Overdraft
Provision for Taxation
Outstanding Expenses
Pre-received Incomes
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 189