Page 95 - DMGT202_COST_AND_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 95
Cost and Management Accounting
Notes
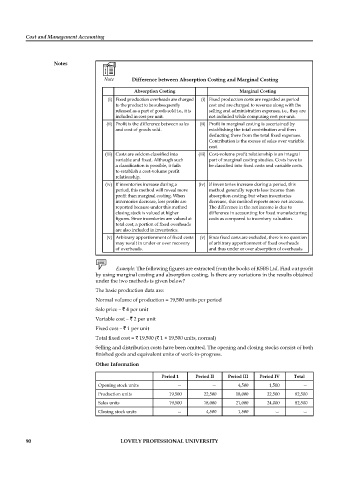
Note Difference between Absorption Costing and Marginal Costing
Absorption Costing Marginal Costing
(i) Fixed production overheads are charged (i) Fixed production costs are regarded as period
to the product to be subsequently cost and are charged to revenue along with the
released as a part of goods sold i.e., it is selling and administration expenses, i.e., they are
included in cost per unit. not included while computing cost per unit.
(ii) Profit is the difference between sales (ii) Profit in marginal costing is ascertained by
and cost of goods sold. establishing the total contribution and then
deducting there from the total fi xed expenses.
Contribution is the excess of sales over variable
cost.
(iii) Costs are seldom classifi ed into (iii) Cost-volume profit relationship is an integral
variable and fixed. Although such part of marginal costing studies. Costs have to
a classification is possible, it fails be classifi ed into fixed costs and variable costs.
to establish a cost-volume profi t
relationship.
(iv) If inventories increase during a (iv) If inventories increase during a period, this
period, this method will reveal more method generally reports less income than
profit than marginal costing. When absorption costing; but when inventories
inventories decrease, less profi ts are decrease, this method reports more net income.
reported because under this method The difference in the net income is due to
closing stock is valued at higher difference in accounting for fi xed manufacturing
figures. Since inventories are valued at costs as compared to inventory valuation.
total cost, a portion of fi xed overheads
are also included in inventories.
(v) Arbitrary apportionment of fi xed costs (v) Since fixed costs are excluded, there is no question
may result in under or over recovery of arbitrary apportionment of fi xed overheads
of overheads. and thus under or over absorption of overheads.
Example: The following figures are extracted from the books of KSBS Ltd. Find out profi t
by using marginal costing and absorption costing. Is there any variations in the results obtained
under the two methods is given below?
The basic production data are:
Normal volume of production = 19,500 units per period
Sale price – ` 4 per unit
Variable cost – ` 2 per unit
Fixed cost – ` 1 per unit
Total fixed cost = ` 19,500 (` 1 × 19,500 units, normal)
Selling and distribution costs have been omitted. The opening and closing stocks consist of both
finished gods and equivalent units of work-in-progress.
Other Information
Period 1 Period II Period III Period IV Total
Opening stock units — — 4,500 1,500 —
Production units 19,500 22,500 18,000 22,500 82,500
Sales units 19,500 18,000 21,000 24,000 82,500
Closing stock units — 4,500 1,500 — —
90 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY