Page 96 - DMGT202_COST_AND_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 96
Unit 6: Marginal Costing and Absorption Costing
Solution: Notes
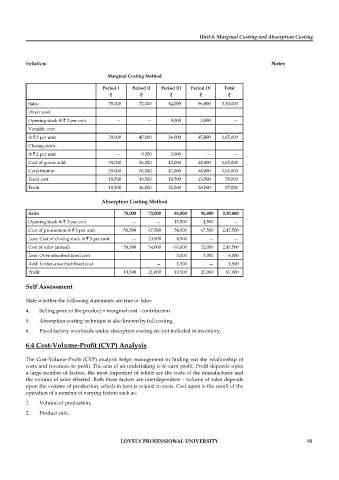
Marginal Costing Method
Period 1 Period II Period III Period IV Total
` ` ` ` `
Sales 78,000 72,000 84,000 96,000 3,30,000
Direct cost:
Opening stock @ ` 2 per unit — — 9,000 3,000 —
Variable cost:
@ ` 2 per unit 39,000 45,000 36,000 45,000 1,65,000
Closing stock:
@ ` 2 per unit — 9,000 3,000 — —
Cost of goods sold 39,000 36,000 42,000 48,000 1,65,000
Contribution 39,000 36,000 42,000 48,000 1,65,000
Fixed cost 19,500 19,500 19,500 19,500 78,000
Profi t 19,500 16,500 22,500 28,500 87,000
Absorption Costing Method
Sales 78,000 72,000 84,000 96,000 3,30,000
Opening stock @ ` 3 per unit — -— 13,500 4,500 —
Cost of production @ ` 3 per unit 58,500 67,500 54,000 67,500 2,47,500
Less: Cost of closing stock @ ` 3 per unit — 13,500 4,500 — —
Cost of sales (actual) 58,500 54,000 63,000 72,000 2,47,500
Less: Over-absorbed fi xed cost 3,000 3,000 6,000
Add: Under-absorbed fi xed cost — 1,500 — 1,500
Profi t 19,500 21,000 19,500 27,000 87,000
Self Assessment
State whether the following statements are true or false:
4. Selling price of the product = marginal cost - contribution.
5. Absorption costing technique is also known by full costing.
6. Fixed factory overheads under absorption costing are not included in inventory.
6.4 Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis
The Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) analysis helps management in finding out the relationship of
costs and revenues to profit. The aim of an undertaking is to earn profi t. Profit depends upon
a large number of factors, the most important of which are the costs of the manufacturer and
the volume of sales effected. Both these factors are interdependent – volume of sales depends
upon the volume of production, which in turn is related to costs. Cost again is the result of the
operation of a number of varying factors such as:
1. Volume of production,
2. Product mix,
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 91