Page 14 - DMGT206_PRODUCTION_AND_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 14
Unit 1: Operations Management Basics
3. Process: There are many ways of producing the product, and Operations Management has Notes
the responsibility of choosing the best way.
4. Program: The production programme ensures that the schedules of production are met.
5. People: Production depends on people and their skills and motivation. Operations
Management has to ensure that skilled and motivated workers are available.
Operations Management, seen in this way, is the science of optimizing transformation processes,
during which ‘sets of inputs’ are converted efficiently and economically into outputs, with the
objective of improving profitability of the organization. We will discuss the components of
Operations Management in the value driven approach. As the value driven approach is broader
based, this traditional view becomes a subset of the larger landscape.
1.2.3 Value Driven Approach
The second approach is a value driven approach to operations management. The value driven
approach starts by recognizing that a business is a ‘set of processes’, each of which has inputs,
outputs, and structure. Each process has a job to do and each process should be measured on how
effective it is in achieving the desired outcomes.
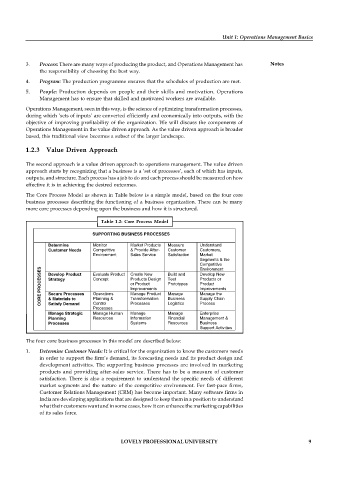
The Core Process Model as shown in Table below is a simple model, based on the four core
business processes describing the functioning of a business organization. There can be many
more core processes depending upon the business and how it is structured.
Table 1.2: Core Process Model
SUPPORTING BUSINESS PROCESSES
Determine Monitor Market Products Measure Understand
Customer Needs Competitive & Provide After- Customer Customers,
Environment Sales Service Satisfaction Market
Segments & the
Competitive
CORE PROCESSES Strategy Concept Products Design Test Products or
Environment
Develop Product
Build and
Develop New
Evaluate Product
Create New
or Product
Prototypes
Product
Improvements
Improvements
Manage Product
Operations
Manage the
Manage
Secure Processes
& Materials to
Planning &
Process
Logistics
Control
Processes
Satisfy Demand
Processes Transformation Business Supply Chain
Manage Strategic Manage Human Manage Manage Enterprise
Planning Resources Information Financial Management &
Processes Systems Resources Business
Support Activities
The four core business processes in this model are described below:
1. Determine Customer Needs: It is critical for the organization to know the customers needs
in order to support the firm’s demand, its forecasting needs and its product design and
development activities. The supporting business processes are involved in marketing
products and providing after-sales service. There has to be a measure of customer
satisfaction. There is also a requirement to understand the specific needs of different
market segments and the nature of the competitive environment. For fast-pace firms,
Customer Relations Management (CRM) has become important. Many software firms in
India are developing applications that are designed to keep them in a position to understand
what their customers want and in some cases, how it can enhance the marketing capabilities
of its sales force.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 9