Page 281 - DMGT207_MANAGEMENT_OF_FINANCES
P. 281
Management of Finances
Notes At the EOQ, the cost of ordering for the period ( 6000) equals the carrying cost for the period
( 6000).
Statement showing total inventory cost at different order size is given below:
SWT Company
Schedule of Inventory Costs at Various Order Sizes
Order Size 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600
Avg Inventory Size 200 300 400 500 600 700 800
No. of Inventory 30 20 15 12 10 8.6 7.5
Orders
Ordering Cost 15000 10000 7500 6000 5000 4300 3750
Carrying Cost 2400 3600 4800 6000 7200 8400 9600
Total Inventory Cost 17400 13600 12300 12000 12200 12700 13350
The above statement also shows that total inventory cost is least at order size of 1000. Any order
sizes other than EOQ level yields a higher total inventory cost.
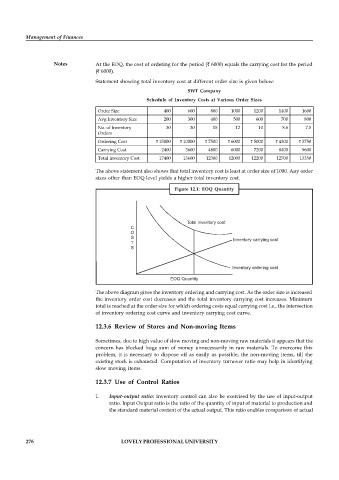
Figure 12.1: EOQ Quantity
Total inventory cost
C
O
S Inventory carrying cost
T
S
Inventory ordering cost
EOQ Quantity
The above diagram gives the inventory ordering and carrying cost. As the order size is increased
the inventory order cost decreases and the total inventory carrying cost increases. Minimum
total is reached at the order size for which ordering costs equal carrying cost i.e., the intersection
of inventory ordering cost curve and inventory carrying cost curve.
12.3.6 Review of Stores and Non-moving Items
Sometimes, due to high value of slow moving and non-moving raw materials it appears that the
concern has blocked huge sum of money unnecessarily in raw materials. To overcome this
problem, it is necessary to dispose off as easily as possible, the non-moving items, till the
existing stock is exhausted. Computation of inventory turnover ratio may help in identifying
slow moving items.
12.3.7 Use of Control Ratios
1. Input-output ratio: Inventory control can also be exercised by the use of input-output
ratio. Input Output ratio is the ratio of the quantity of input of material to production and
the standard material content of the actual output. This ratio enables comparison of actual
276 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY