Page 216 - DENG401_Advance Communication Skills
P. 216
Unit 12: Subordinating Conjunctions
Since: You are coming Notes
These are not complete sentence. They all have subjects (you, I, you) and verbs (are, see, are
coming) but since they cannot stand alone. But unlike a subordinate clause, an independent
clause can stand alone.
Subordinating conjunctions but us join subordinate clause with independent clause.
Example: 1. I will bring my cat unless you are allergic.
2. Whenever I see your cat I sneeze.
3. Since you are coming. I won’t bring my cat.
Independent Clause:
I will bring my cat
I sneeze
I won’t bring my cat.
These are all complete sentence. They all have subject (I), verb (will bring, sneeze, won’t bring)
and they can stand alone. Subordinating conjunctions are used to join a dependent clause
(incomplete thought) to an independent clause.
Notes Some sentences are complex. Such sentences have two clauses, one main (or
independent) and one subordinate (or dependent). These are the patterns for a complex
sentence:
Main clause + + subordinate clause.
Subordinate clause + , + main clause
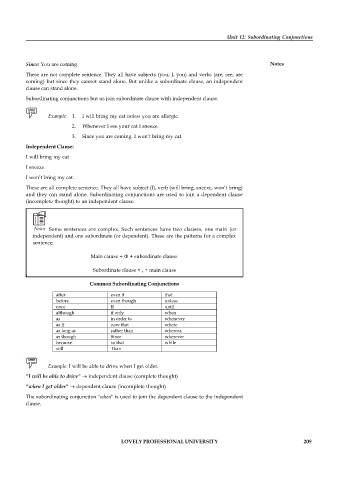
Common Subordinating Conjunctions
after even if that
before even though unless
once If until
although if only when
as in order to whenever
as if now that where
as long as rather than whereas
as though Since wherever
because so that while
still Than
Example: I will be able to drive when I get older.
"I will be able to drive" independent clause (complete thought)
"when I get older" dependent clause (incomplete thought)
The subordinating conjunction "when" is used to join the dependent clause to the independent
clause.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 209