Page 287 - DMGT402_MANAGEMENT_PRACTICES_AND_ORGANIZATIONAL_BEHAVIOUR
P. 287
Management Practices and Organisational Behaviour
Notes (c) Leader position power: The most obvious manner in which the leader secures power is
by accepting and performing the leadership role. Position power in the contingency
model refers to the power inherent in the leader's organisational position. It refers
to the degree to which the leader has at his disposal various rewards and sanctions,
his authority over group's members, and the degree to which this authority is
supported by the organisation.
(d) Favourableness of the situation: Thus, depending on the 'high' and low' categories of
these situational variables, Fiedler developed eight possible combinations ranging
from highly favourable to unfavourable situations.
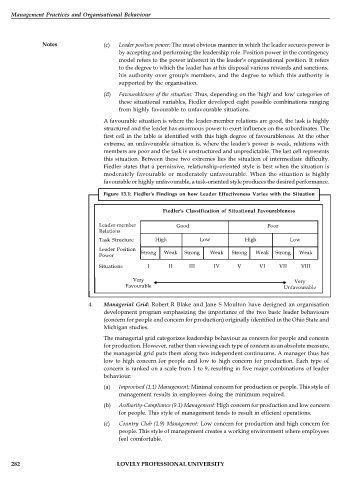
A favourable situation is where the leader-member relations are good, the task is highly
structured and the leader has enormous power to exert influence on the subordinates. The
first cell in the table is identified with this high degree of favourableness. At the other
extreme, an unfavourable situation is, where the leader's power is weak, relations with
members are poor and the task is unstructured and unpredictable. The last cell represents
this situation. Between these two extremes lies the situation of intermediate difficulty.
Fiedler states that a permissive, relationship-oriented style is best when the situation is
moderately favourable or moderately unfavourable. When the situation is highly
favourable or highly unfavourable, a task-oriented style produces the desired performance.
Figure 13.1: Fiedler's Findings on how Leader Effectiveness Varies with the Situation
Fiedler's Classification of Situational Favourableness
Leader-member Good Poor
Relations
Task Structure High Low High Low
Leader Position Strong Weak Strong Weak Strong Weak Strong Weak
Power
Situations I II III IV V VI VII VIII
Very Very
Favourable Unfavourable
4. Managerial Grid: Robert R Blake and Jane S Moulton have designed an organisation
development program emphasizing the importance of the two basic leader behaviours
(concern for people and concern for production) originally identified in the Ohio State and
Michigan studies.
The managerial grid categorizes leadership behaviour as concern for people and concern
for production. However, rather than viewing each type of concern as an absolute measure,
the managerial grid puts them along two independent continuums. A manager thus has
low to high concern for people and low to high concern for production. Each type of
concern is ranked on a scale from 1 to 9, resulting in five major combinations of leader
behaviour:
(a) Improvised (1,1) Management: Minimal concern for production or people. This style of
management results in employees doing the minimum required.
(b) Authority-Compliance (9.1) Management: High concern for production and low concern
for people. This style of management tends to result in efficient operations.
(c) Country Club (1,9) Management: Low concern for production and high concern for
people. This style of management creates a working environment where employees
feel comfortable.
282 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY