Page 348 - DMGT402_MANAGEMENT_PRACTICES_AND_ORGANIZATIONAL_BEHAVIOUR
P. 348
Unit 16: Organisational Culture
2. List the forces driving change on the arrows at the left side of the diagram. Notes
3. List the forces restraining change on the arrows at the right side of the diagram.
4. What can you do, specifically, to remove the obstacles to change?
5. What can you do to increase the forces driving change?
6. What benefits can be derived from breaking a problem down into forces driving
change and forces restraining change?
Forces driving change Forces restraining change
Source: Debra L Nelson and James Campbell Quick, Organisation Behaviour – Foundations, Realities and
Challenges (Second Edition), West Publishing Company, Minneapolis (1997) Page 553.
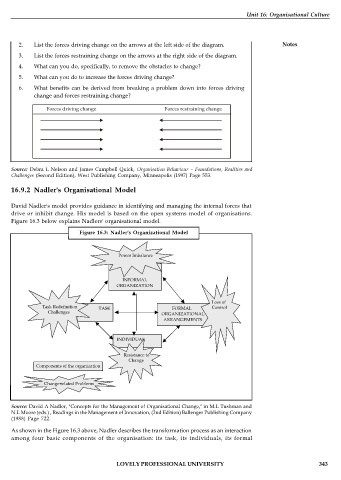
16.9.2 Nadler's Organisational Model
David Nadler's model provides guidance in identifying and managing the internal forces that
drive or inhibit change. His model is based on the open systems model of organisations.
Figure 16.3 below explains Nadlers' organisational model.
Figure 16.3: Nadler's Organizational Model
Power Imbalance
INFORMAL
ORGANIZATION
Loss of
Task Redefinition Control
TASK FORMAL
Challenges
ORGANIZATIONAL
ARRANGEMENTS
INDIVIDUAL
Resistance to
Change
Components of the organization
-
Change related Problems
Source: David A Nadler, "Concepts for the Management of Organisational Change," in M.L Tushman and
N.L Moore (eds.) , Readings in the Management of Innovation, (2nd Edition) Ballenger Publishing Company
(1988) Page 722.
As shown in the Figure 16.3 above, Nadler describes the transformation process as an interaction
among four basic components of the organisation: its task, its individuals, its formal
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 343