Page 41 - DMGT403_ACCOUNTING_FOR_MANAGERS
P. 41
Accounting for Managers
Notes
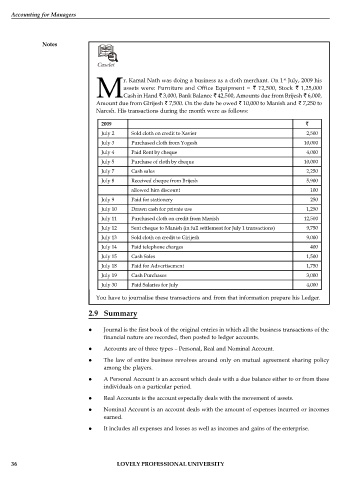
Caselet
st
r. Kamal Nath was doing a business as a cloth merchant. On 1 July, 2009 his
assets were: Furniture and Office Equipment = 12,500, Stock 1,25,000
MCash in Hand 3,000, Bank Balance 42,500, Amounts due from Brijesh 6,000,
Amount due from Girijesh 7,500. On the date he owed 10,000 to Manish and 7,250 to
Naresh. His transactions during the month were as follows:
2009
July 2 Sold cloth on credit to Xavier 2,500
July 3 Purchased cloth from Yogesh 10,000
July 4 Paid Rent by cheque 4,000
July 5 Purchase of cloth by cheque 10,000
July 7 Cash sales 2,250
July 8 Received cheque from Brijesh 5,900
allowed him discount 100
July 9 Paid for stationery 250
July 10 Drawn cash for private use 1,250
July 11 Purchased cloth on credit from Manish 12,500
July 12 Sent cheque to Manish (in full settlement for July 1 transactions) 9,750
July 13 Sold cloth on credit to Girijesh 9,000
July 14 Paid telephone charges 400
July 15 Cash Sales 1,500
July 18 Paid for Advertisement 1,750
July 19 Cash Purchases 3,000
July 30 Paid Salaries for July 4,000
You have to journalise these transactions and from that information prepare his Ledger.
2.9 Summary
Journal is the first book of the original entries in which all the business transactions of the
financial nature are recorded, then posted to ledger accounts.
Accounts are of three types – Personal, Real and Nominal Account.
The law of entire business revolves around only on mutual agreement sharing policy
among the players.
A Personal Account is an account which deals with a due balance either to or from these
individuals on a particular period.
Real Accounts is the account especially deals with the movement of assets.
Nominal Account is an account deals with the amount of expenses incurred or incomes
earned.
It includes all expenses and losses as well as incomes and gains of the enterprise.
36 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY