Page 103 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 103
Unit 5: Measurement and Scaling Techniques
Notes
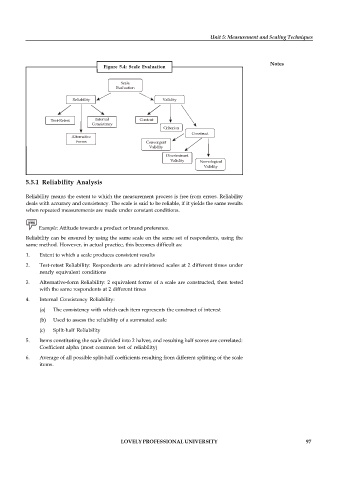
Figure 5.4: Scale Evaluation
Scale
Evaluation
Reliability Validity
Test-Retest Internal Content
Consistency
Criterion
Construct
Alternative
Forms Convergent
Validity
Discriminant
Validity Nomological
Validity
5.5.1 Reliability Analysis
Reliability means the extent to which the measurement process is free from errors. Reliability
deals with accuracy and consistency. The scale is said to be reliable, if it yields the same results
when repeated measurements are made under constant conditions.
Example: Attitude towards a product or brand preference.
Reliability can be ensured by using the same scale on the same set of respondents, using the
same method. However, in actual practice, this becomes difficult as:
1. Extent to which a scale produces consistent results
2. Test-retest Reliability: Respondents are administered scales at 2 different times under
nearly equivalent conditions
3. Alternative-form Reliability: 2 equivalent forms of a scale are constructed, then tested
with the same respondents at 2 different times
4. Internal Consistency Reliability:
(a) The consistency with which each item represents the construct of interest
(b) Used to assess the reliability of a summated scale
(c) Split-half Reliability
5. Items constituting the scale divided into 2 halves, and resulting half scores are correlated:
Coefficient alpha (most common test of reliability)
6. Average of all possible split-half coefficients resulting from different splitting of the scale
items.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 97