Page 262 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 262
Research Methodology
Notes There are two types of tests.
One-tailed and Two-tailed Tests
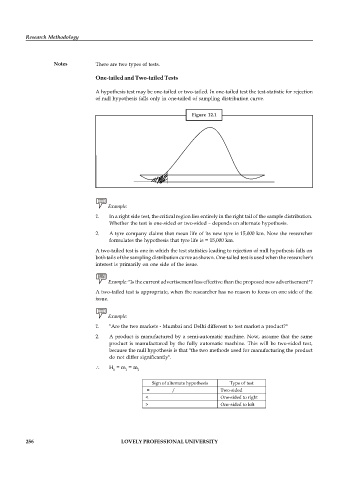
A hypothesis test may be one-tailed or two-tailed. In one-tailed test the test-statistic for rejection
of null hypothesis falls only in one-tailed of sampling distribution curve.
Figure 12.1
Example:
1. In a right side test, the critical region lies entirely in the right tail of the sample distribution.
Whether the test is one-sided or two-sided – depends on alternate hypothesis.
2. A tyre company claims that mean life of its new tyre is 15,000 km. Now the researcher
formulates the hypothesis that tyre life is = 15,000 km.
A two-tailed test is one in which the test statistics leading to rejection of null hypothesis falls on
both tails of the sampling distribution curve as shown. One-tailed test is used when the researcher's
interest is primarily on one side of the issue.
Example: "Is the current advertisement less effective than the proposed new advertisement"?
A two-tailed test is appropriate, when the researcher has no reason to focus on one side of the
issue.
Example:
1. "Are the two markets - Mumbai and Delhi different to test market a product?"
2. A product is manufactured by a semi-automatic machine. Now, assume that the same
product is manufactured by the fully automatic machine. This will be two-sided test,
because the null hypothesis is that "the two methods used for manufacturing the product
do not differ significantly".
H = m = m
0 1 2
Sign of alternate hypothesis Type of test
= / Two-sided
< One-sided to right
> One-sided to left
256 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY