Page 11 - DMGT408DMGT203_Marketing Management
P. 11
Marketing Management/Essentials of Marketing
Notes
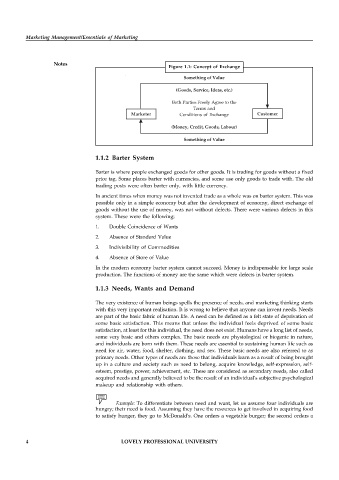
Figure 1.1: Concept of Exchange
Something of Value
(Goods, Service, Ideas, etc.)
Both Parties Freely Agree to the
Terms and
Marketer Conditions of Exchange Customer
(Money, Credit, Goods, Labour)
Something of Value
1.1.2 Barter System
Barter is where people exchanged goods for other goods. It is trading for goods without a fixed
price tag. Some places barter with currencies, and some use only goods to trade with. The old
trading posts were often barter only, with little currency.
In ancient times when money was not invented trade as a whole was on barter system. This was
possible only in a simple economy but after the development of economy, direct exchange of
goods without the use of money, was not without defects. There were various defects in this
system. These were the following;
1. Double Coincidence of Wants
2. Absence of Standard Value
3. Indivisibility of Commodities
4. Absence of Store of Value
In the modern economy barter system cannot succeed. Money is indispensable for large scale
production. The functions of money are the same which were defects in barter system.
1.1.3 Needs, Wants and Demand
The very existence of human beings spells the presence of needs, and marketing thinking starts
with this very important realisation. It is wrong to believe that anyone can invent needs. Needs
are part of the basic fabric of human life. A need can be defined as a felt state of deprivation of
some basic satisfaction. This means that unless the individual feels deprived of some basic
satisfaction, at least for this individual, the need does not exist. Humans have a long list of needs,
some very basic and others complex. The basic needs are physiological or biogenic in nature,
and individuals are born with them. These needs are essential to sustaining human life such as
need for air, water, food, shelter, clothing, and sex. These basic needs are also referred to as
primary needs. Other types of needs are those that individuals learn as a result of being brought
up in a culture and society such as need to belong, acquire knowledge, self-expression, self-
esteem, prestige, power, achievement, etc. These are considered as secondary needs, also called
acquired needs and generally believed to be the result of an individual's subjective psychological
makeup and relationship with others.
Example: To differentiate between need and want, let us assume four individuals are
hungry; their need is food. Assuming they have the resources to get involved in acquiring food
to satisfy hunger, they go to McDonald's. One orders a vegetable burger; the second orders a
4 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY