Page 227 - DCAP302_ENTERPRISE_RESOURCE_PLANNING
P. 227
Unit 14: Case Study – ERP Application on Supply Chain
notes
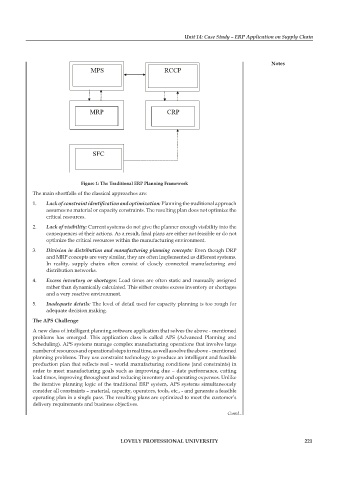
MPS RCCP
MRP CRP
SFC
figure 1: the traditional erp planning framework
The main shortfalls of the classical approaches are:
1. Lack of constraint identification and optimization: Planning the traditional approach
assumes no material or capacity constraints. The resulting plan does not optimize the
critical resources.
2. Lack of visibility: Current systems do not give the planner enough visibility into the
consequences of their actions. As a result, final plans are either not feasible or do not
optimize the critical resources within the manufacturing environment.
3. Division in distribution and manufacturing planning concepts: Even though DRP
and MRP concepts are very similar, they are often implemented as different systems.
In reality, supply chains often consist of closely connected manufacturing and
distribution networks.
4. Excess inventory or shortages: Lead times are often static and manually assigned
rather than dynamically calculated. This either creates excess inventory or shortages
and a very reactive environment.
5. Inadequate details: The level of detail used for capacity planning is too rough for
adequate decision making.
the aps challenge
A new class of intelligent planning software application that solves the above - mentioned
problems has emerged. This application class is called APS (Advanced Planning and
Scheduling). APS systems manage complex manufacturing operations that involve large
number of resources and operational steps in real time, as well as solve the above – mentioned
planning problems. They use constraint technology to produce an intelligent and feasible
production plan that reflects real – world manufacturing conditions (and constraints) in
order to meet manufacturing goals such as improving due – date performance, cutting
lead times, improving throughout and reducing inventory and operating expenses. Unlike
the iterative planning logic of the traditional ERP system, APS systems simultaneously
consider all constraints – material, capacity, operators, tools, etc., - and generate a feasible
operating plan in a single pass. The resulting plans are optimized to meet the customer’s
delivery requirements and business objectives.
Contd...
LoveLy professionaL university 221