Page 109 - DMGT501_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 109
Unit 4: Process Selection and Facility Layout
Space requirements also need to be computed. Based on the size and number of machines to be Notes
installed and the space available for the layout, the minimum space required is worked out. The
requirement of space for each department, for Anand Parvat Industries, is shown in Table 4.2.
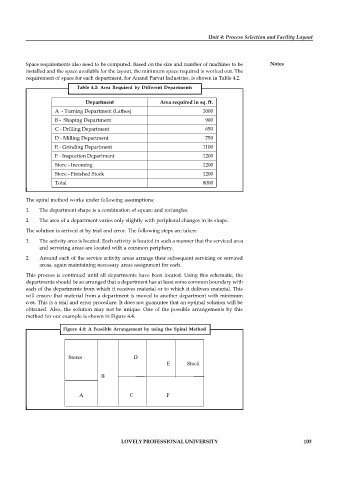
Table 4.2: Area Required by Different Departments
Department Area required in sq. ft.
A - Turning Department (Lathes) 1000
B - Shaping Department 900
C - Drilling Department 650
D - Milling Department 750
E - Grinding Department 1100
F - Inspection Department 1200
Store - Incoming 1200
Store - Finished Stock 1200
Total 8000
The spiral method works under following assumptions:
1. The department shape is a combination of square and rectangles.
2. The area of a department varies only slightly with peripheral changes in its shape.
The solution is arrived at by trial and error. The following steps are taken:
1. The activity area is located. Each activity is located in such a manner that the serviced area
and servicing areas are located with a common periphery.
2. Around each of the service activity areas arrange their subsequent servicing or serviced
areas, again maintaining necessary areas assignment for each.
This process is continued until all departments have been located. Using this schematic, the
departments should be so arranged that a department has at least some common boundary with
each of the departments from which it receives material or to which it delivers material. This
will ensure that material from a department is moved to another department with minimum
cost. This is a trial and error procedure. It does not guarantee that an optimal solution will be
obtained. Also, the solution may not be unique. One of the possible arrangements by this
method for our example is shown in Figure 4.4.
Figure 4.4: A Feasible Arrangement by using the Spiral Method
Stores D
E Stock
B
A C F
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 103