Page 93 - DMGT506_CONSUMER_BEHAVIOUR
P. 93
Consumer Behaviour
Notes
Example: Almost everyday we see commercials of one or the other detergent depicting
the agony of a mother or housewife washing clothes, dissatisfied or embarrassed and ultimately
finding the rewarding experience with a particular (advertised) brand of detergent. The message
for the target audience is loud and clear that to avoid unfavourable outcomes with other
detergents, they should use the advertised brand. There are other similar commercials such as
those of common cold remedies (readers might be familiar with Coldarin commercial), balms
for waist and joint pains, pimple and acne remedies, anti-itch creams, antidandruff shampoos
and deodorants etc. The common theme is the same in all the commercials that to avoid uneasy
feelings and embarrassment, consumers should use the advertised product.
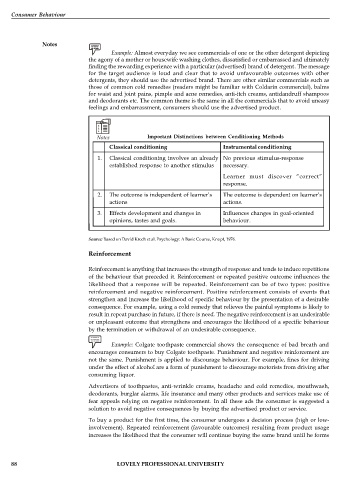
Notes Important Distinctions between Conditioning Methods
Classical conditioning Instrumental conditioning
1. Classical conditioning involves an already No previous stimulus-response
established response to another stimulus necessary.
Learner must discover “correct”
response.
2. The outcome is independent of learner’s The outcome is dependent on learner’s
actions actions.
3. Effects development and changes in Influences changes in goal-oriented
opinions, tastes and goals. behaviour.
Source: Based on David Krech et al. Psychology: A Basic Course, Knopf, 1976.
Reinforcement
Reinforcement is anything that increases the strength of response and tends to induce repetitions
of the behaviour that preceded it. Reinforcement or repeated positive outcome influences the
likelihood that a response will be repeated. Reinforcement can be of two types: positive
reinforcement and negative reinforcement. Positive reinforcement consists of events that
strengthen and increase the likelihood of specific behaviour by the presentation of a desirable
consequence. For example, using a cold remedy that relieves the painful symptoms is likely to
result in repeat purchase in future, if there is need. The negative reinforcement is an undesirable
or unpleasant outcome that strengthens and encourages the likelihood of a specific behaviour
by the termination or withdrawal of an undesirable consequence.
Example: Colgate toothpaste commercial shows the consequence of bad breath and
encourages consumers to buy Colgate toothpaste. Punishment and negative reinforcement are
not the same. Punishment is applied to discourage behaviour. For example, fines for driving
under the effect of alcohol are a form of punishment to discourage motorists from driving after
consuming liquor.
Advertisers of toothpastes, anti-wrinkle creams, headache and cold remedies, mouthwash,
deodorants, burglar alarms, life insurance and many other products and services make use of
fear appeals relying on negative reinforcement. In all these ads the consumer is suggested a
solution to avoid negative consequences by buying the advertised product or service.
To buy a product for the first time, the consumer undergoes a decision process (high or low-
involvement). Repeated reinforcement (favourable outcomes) resulting from product usage
increases the likelihood that the consumer will continue buying the same brand until he forms
88 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY