Page 237 - DMGT545_INTERNATIONAL_BUSINESS
P. 237
International Business
notes advantages. First, it enables the firm to make the best use of its human resources. Second,
and perhaps more important, a geocentric policy enables the firm to build a cadre of
international executives who feel at home working in a number of cultures. Creation of such
a cadre may be a critical first step toward building a strong unifying corporate culture and
an informal management network, both of which are required for global standardization
and transnational strategies. Firms pursuing a geocentric staffing policy may be better able
to create value from the pursuit of experience curve and location economies and from the
multidirectional transfer of core competencies than firms pursuing other staffing policies.
In addition, the multinational composition of the management team that results from
geocentric staffing tends to reduce cultural myopia and to enhance local responsiveness.
Thus, other things being equal, a geocentric staffing policy seems the most attractive.
A number of problems limit the firm’s ability to pursue a geocentric policy. Many countries want
foreign subsidiaries to employ their citizens. To achieve this goal, they use immigration laws to
require the employment of host-country nationals if they are available in adequate numbers and
have the necessary skills. Most countries (including the United States) require firms to provide
extensive documentation if they wish to hire a foreign national instead of a local national. This
documentation can be time consuming, expensive, and at times futile. A geocentric staffing
policy also can be very expensive to implement. Training and relocation costs increase when
transferring managers from country to country. The company may also need a compensation
structure with a standardized international base pay level higher than national levels in many
countries. In addition, the higher pay enjoyed by managers placed on an international ‘fast track’
may be a source of resentment within a firm.
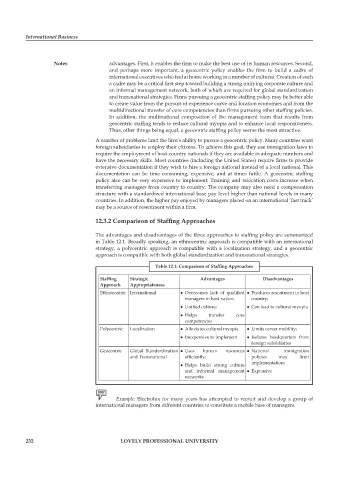
12.3.2 Comparison of Staffing Approaches
The advantages and disadvantages of the three approaches to staffing policy are summarized
in Table 12.1. Broadly speaking, an ethnocentric approach is compatible with an international
strategy, a polycentric approach is compatible with a localization strategy, and a geocentric
approach is compatible with both global standardization and transnational strategies.
Table 12.1: Comparison of Staffing Approaches
Staffing strategic advantages Disadvantages
approach appropriateness
Ethnocentric International l Overcomes lack of qualified l Produces resentment in host
managers in host nation; country;
l Unified culture; l Can lead to cultural myopia
l Helps transfer core
competencies
Polycentric Localization l Alleviates cultural myopia l Limits career mobility;
l Inexpensive to implement l Isolates headquarters from
foreign subsidiaries
Geocentric Global Standardization l Uses human resources l National immigration
and Transnational efficiently; policies may limit
l Helps build strong culture implementation;
and informal management l Expensive
networks
Example: Electrolux for many years has attempted to recruit and develop a group of
international managers from different countries to constitute a mobile base of managers.
232 lovely Professional university