Page 276 - DMGT546_INTERNATIONAL_TRADE_PROCEDURE_AND_DOCUMENTATION
P. 276
Unit 13: Special Economic Zones
Notes
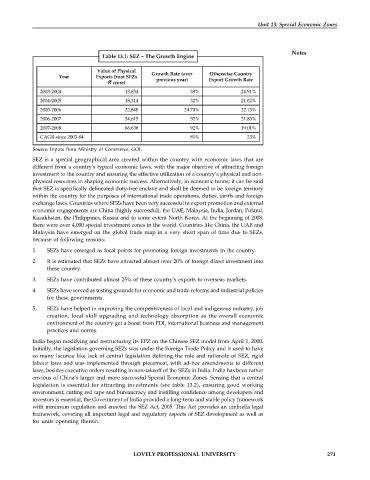
Table 13.1: SEZ – The Growth Engine
Value of Physical Growth Rate (over Otherwise Country
Year Exports from SEZs previous year) Export Growth Rate
(` crore)
2003-2004 13,854 39% 24.91%
2004-2005 18,314 32% 21.62%
2005-2006 22,840 24.70% 22.13%
2006-2007 34,615 52% 21.83%
2007-2008 66,638 92% 19.01%
CAGR since 2003-04 81% 23%
Source: Inputs from Ministry of Commerce, GOI.
SEZ is a special geographical area created within the country with economic laws that are
different from a country’s typical economic laws, with the major objective of attracting foreign
investment to the country and ensuring the effective utilization of a country’s physical and non-
physical resources in shaping economic success. Alternatively, in economic terms; it can be said
that SEZ is specifically delineated duty-free enclave and shall be deemed to be foreign territory
within the country for the purposes of international trade operations, duties, tariffs and foreign
exchange laws. Countries where SEZs have been very successful in export promotion and external
economic engagements are China (highly successful), the UAE, Malaysia, India, Jordan, Poland,
Kazakhstan, the Philippines, Russia and to some extent North Korea. At the beginning of 2008,
there were over 4,000 special investment zones in the world. Countries like China, the UAE and
Malaysia have emerged on the global trade map in a very short span of time due to SEZs,
because of following reasons:
1. SEZs have emerged as focal points for promoting foreign investments in the country.
2. It is estimated that SEZs have attracted almost over 20% of foreign direct investment into
these country.
3. SEZs have contributed almost 25% of these country’s exports to overseas markets.
4. SEZs have served as testing grounds for economic and trade reforms and industrial policies
for these governments.
5. SEZs have helped in improving the competitiveness of local and indigenous industry, job
creation, local skill upgrading and technology absorption as the overall economic
environment of the country get a boost from FDI, international business and management
practices and norms.
India began modifying and restructuring its EPZ on the Chinese SEZ model from April 1, 2000.
Initially, the legislation governing SEZs was under the Foreign Trade Policy and it used to have
so many lacunae like lack of central legislation defining the role and rationale of SEZ, rigid
labour laws and was implemented through piecemeal, with ad-hoc amendments to different
laws, besides executive orders resulting in non-takeoff of the SEZs in India. India has been rather
envious of China’s larger and more successful Special Economic Zones. Sensing that a central
legislation is essential for attracting investments (see table 13.2), ensuring good working
environment, cutting red tape and bureaucracy and instilling confidence among developers and
investors is essential, the Government of India provided a long-term and stable policy framework
with minimum regulation and enacted the SEZ Act, 2005. This Act provides an umbrella legal
framework, covering all important legal and regulatory aspects of SEZ development as well as
for units operating therein.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 271