Page 258 - DCAP304_DCAP515_SOFTWARE_PROJECT_MANAGEMENT
P. 258
Software Project Management
Notes Positive variances bring their own set of problems, which can be as serious as negative variances.
Positive variances can allow for rescheduling to bring the project to completion early, under
budget, or both. Resources can be reallocated from ahead-of-schedule projects to behind-schedule
projects.
Negative Variances
Negative variances are deviations from plan that indicate that a behind-schedule situation has
occurred or that an actual cost was greater than a planned cost.
Negative variances, just like positive variances, are not necessarily bad news. For example, you
might have overspent because you accomplished more work during the report period than was
planned. But in overspending during this period, you could have accomplished the work at less
cost than was originally planned. You can’t tell by looking at the variance report.
In most cases, negative time variances affect project completion only if they are associated with
critical path activities or if the schedule slippage on non-critical path activities exceeds the
activity’s total float. Variances use up the float time for that activity; more serious ones will
cause a change in the critical path.
Negative cost variances can result from uncontrollable factors such as cost increases from suppliers
or unexpected equipment malfunctions. Some negative variances can result from inefficiencies
or error.
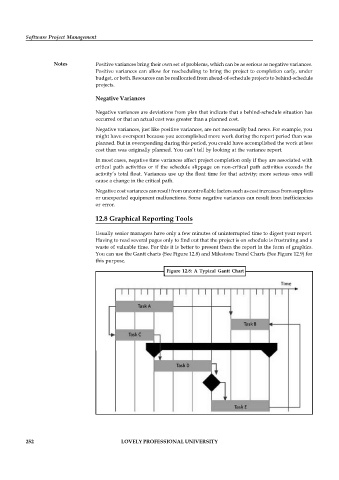
12.8 Graphical Reporting Tools
Usually senior managers have only a few minutes of uninterrupted time to digest your report.
Having to read several pages only to find out that the project is on schedule is frustrating and a
waste of valuable time. For this it is better to present them the report in the form of graphics.
You can use the Gantt charts (See Figure 12.8) and Milestone Trend Charts (See Figure 12.9) for
this purpose.
Figure 12.8: A Typical Gantt Chart
252 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY