Page 210 - DCOM303_DMGT504_OPERATION_RESEARCH
P. 210
Unit 10: Sequencing Problems and Replacement Theory
Since either one of the conditions is satisfied, the problem can now be converted into two- Notes
machine type.
Assuming imaginary machines as M and M (see Table 6.33,)
4 5
Where, M = M + M and,
4 1 2
M = M + M
5 2 3
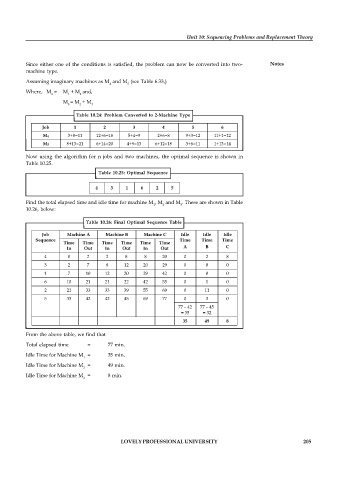
Table 10.24: Problem Converted to 2-Machine Type
Job 1 2 3 4 5 6
M4 3+8=11 12+6=18 5+4=9 2+6=8 9+3=12 11+1=12
M5 8+13=21 6+14=20 4+9=13 6+12=18 3+8=11 1+13=14
Now using the algorithm for n jobs and two machines, the optimal sequence is shown in
Table 10.25.
Table 10.25: Optimal Sequence
4 3 1 6 2 5
Find the total elapsed time and idle time for machine M , M and M . These are shown in Table
1 2 3
10.26, below:
Table 10.26: Final Optimal Sequence Table
Job Machine A Machine B Machine C Idle Idle Idle
Sequence Time Time Time
Time Time Time Time Time Time
In Out In Out In Out A B C
4 0 2 2 8 8 20 0 2 8
3 2 7 8 12 20 29 0 0 0
1 7 10 12 20 29 42 0 0 0
6 10 21 21 22 42 55 0 1 0
2 21 33 33 39 55 69 0 11 0
5 33 42 42 45 69 77 0 3 0
77 – 42 77 – 45
= 35 = 32
35 49 8
From the above table, we find that
Total elapsed time = 77 min.
Idle Time for Machine M = 35 min.
1
Idle Time for Machine M = 49 min.
2
Idle Time for Machine M = 8 min.
3
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 205