Page 250 - DCOM303_DMGT504_OPERATION_RESEARCH
P. 250
Unit 12: Critical Path Method and PERT
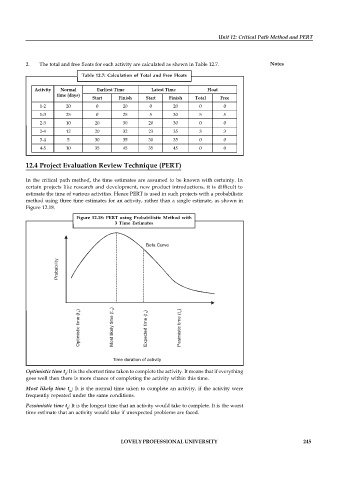
2. The total and free floats for each activity are calculated as shown in Table 12.7. Notes
Table 12.7: Calculation of Total and Free Floats
Activity Normal Earliest Time Latest Time Float
time (days)
Start Finish Start Finish Total Free
1-2 20 0 20 0 20 0 0
1-3 25 0 25 5 30 5 5
2-3 10 20 30 20 30 0 0
2-4 12 20 32 23 35 3 3
3-4 5 30 35 30 35 0 0
4-5 10 35 45 35 45 0 0
12.4 Project Evaluation Review Technique (PERT)
In the critical path method, the time estimates are assumed to be known with certainty. In
certain projects like research and development, new product introductions, it is difficult to
estimate the time of various activities. Hence PERT is used in such projects with a probabilistic
method using three time estimates for an activity, rather than a single estimate, as shown in
Figure 12.18.
Figure 12.18: PERT using Probabilistic Method with
3 Time Estimates
Beta Curve
Probability
)
) ) )
Optimistic time (t 0 Most likely time (t m Expected time (t e Pesimistic time (t p
Time duration of activity
Optimistic time t : It is the shortest time taken to complete the activity. It means that if everything
0
goes well then there is more chance of completing the activity within this time.
Most likely time t : It is the normal time taken to complete an activity, if the activity were
m
frequently repeated under the same conditions.
Pessimistic time t : It is the longest time that an activity would take to complete. It is the worst
p
time estimate that an activity would take if unexpected problems are faced.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 245