Page 246 - DMGT505_MANAGEMENT_INFORMATION_SYSTEM
P. 246
Unit 13: Redesigning the Organization with Information Systems
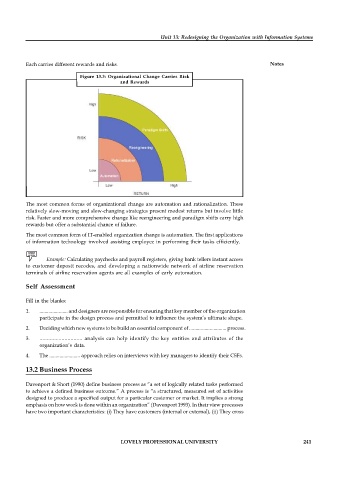
Each carries different rewards and risks. Notes
Figure 13.3: Organizational Change Carries Risk
and Rewards
The most common forms of organizational change are automation and rationalization. These
relatively slow-moving and slow-changing strategies present modest returns but involve little
risk. Faster and more comprehensive change like reengineering and paradigm shifts carry high
rewards but offer a substantial chance of failure.
The most common form of IT-enabled organization change is automation. The first applications
of information technology involved assisting employee in performing their tasks efficiently.
Example: Calculating paychecks and payroll registers, giving bank tellers instant access
to customer deposit recodes, and developing a nationwide network of airline reservation
terminals of airline reservation agents are all examples of early automation.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
1. ...................... and designers are responsible for ensuring that key member of the organization
participate in the design process and permitted to influence the system’s ultimate shape.
2. Deciding which new systems to be build an essential component of ............................. process.
3. ............................. analysis can help identify the key entities and attributes of the
organization’s data.
4. The ........................ approach relies on interviews with key managers to identify their CSFs.
13.2 Business Process
Davenport & Short (1990) define business process as “a set of logically related tasks performed
to achieve a defined business outcome.” A process is “a structured, measured set of activities
designed to produce a specified output for a particular customer or market. It implies a strong
emphasis on how work is done within an organization” (Davenport 1993). In their view processes
have two important characteristics: (i) They have customers (internal or external), (ii) They cross
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 241