Page 35 - DMGT513_DERIVATIVES_AND_RISK_MANAGEMENT
P. 35
Derivatives & Risk Management
Notes price of cable rises during that time. By entering into this agreement with the cable company,
you have reduced your risk of higher prices.
3.2.1 Classification of Forward Contracts
Forward contracts in India are broadly governed by the Forward Contracts (regulation) Act,
1952. According to this act, forward contracts are of the following three major categories.
1. Hedge Contracts: These are freely transferable contracts which do not require specification
of a particular lot size, quality or delivery standards for the underlying assets. Most of
these are necessary to be settled through delivery of underlying assets.
2. Transferable Specific Delivery Forward Contracts: Apart from being freely transferable
between parties concerned, these forward contracts refer to a specific and predetermined
lot size and variety of the underlying asset. It is compulsory for delivery of the underlying
assets to take place at expiration of contract.
3. Non-transferable Specific Delivery Forward Contracts: These contracts are normally
exempted from the provision of regulation under Forward Contract Act, 1952 but the
Central Government reserves the right to bring them back under the Act when it feels
necessary. These are contracts which cannot be transferred to another party. The contracts,
the consignment lot size, and quality of underlying asset are required to be settled at
expiration through delivery of the assets.
3.2.2 Forward Contract Mechanism
The trading mechanism of forward contracts can be better understood through the following
example.
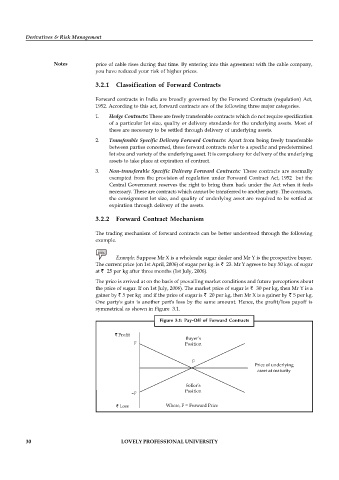
Example: Suppose Mr X is a wholesale sugar dealer and Mr Y is the prospective buyer.
The current price (on 1st April, 2006) of sugar per kg. is ` 23. Mr Y agrees to buy 50 kgs. of sugar
at ` 25 per kg after three months (1st July, 2006).
The price is arrived at on the basis of prevailing market conditions and future perceptions about
the price of sugar. If on 1st July, 2006). The market price of sugar is ` 30 per kg, then Mr Y is a
gainer by ` 5 per kg and if the price of sugar is ` 20 per kg, then Mr X is a gainer by ` 5 per kg.
One party's gain is another part's loss by the same amount. Hence, the profit/loss payoff is
symmetrical as shown in Figure 3.1.
Figure 3.1: Pay-Off of Forward Contracts
` Profit
Buyer’s
F Position
F
Price of underlying
asset at maturity
Seller’s
Position
–F
` Loss Where, F = Forward Price
30 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY