Page 46 - DMGT513_DERIVATIVES_AND_RISK_MANAGEMENT
P. 46
Unit 4: Future Contracts
Notes
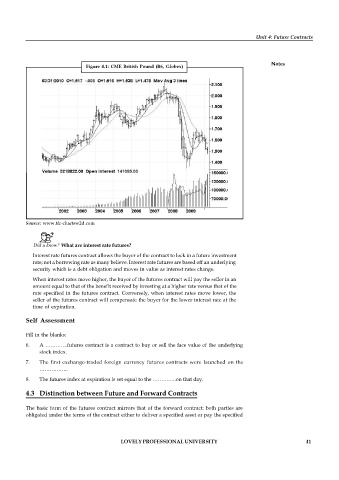
Figure 4.1: CME British Pound (B6, Globex)
Source: www.tfc-chartsw2d.com
Did u know? What are interest rate futures?
Interest rate futures contract allows the buyer of the contract to lock in a future investment
rate; not a borrowing rate as many believe. Interest rate futures are based off an underlying
security which is a debt obligation and moves in value as interest rates change.
When interest rates move higher, the buyer of the futures contract will pay the seller in an
amount equal to that of the benefit received by investing at a higher rate versus that of the
rate specified in the futures contract. Conversely, when interest rates move lower, the
seller of the futures contract will compensate the buyer for the lower interest rate at the
time of expiration.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
6. A ………….futures contract is a contract to buy or sell the face value of the underlying
stock index.
7. The first exchange-traded foreign currency futures contracts were launched on the
……………..
8. The futures index at expiration is set equal to the …………..on that day.
4.3 Distinction between Future and Forward Contracts
The basic form of the futures contract mirrors that of the forward contract: both parties are
obligated under the terms of the contract either to deliver a specified asset or pay the specified
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 41