Page 49 - DMGT513_DERIVATIVES_AND_RISK_MANAGEMENT
P. 49
Derivatives & Risk Management
Notes Self Assessment
State the following are true or false:
9. The value of the futures contract is 'settled' (i.e., paid or received) at the end of each trading
day.
10. A forward contract is an exchange-traded contract.
11. The organization of futures trading with a clearing house reduces the default risks of
trading.
4.4 Pay-Offs
The pay-offs can be categorised as follows:
4.4.1 Payoff for Buyer of Futures: Long Futures
The payoff for a person who buys a futures contract is similar to the payoff for a person who
holds an asset. He has a potentially unlimited upside as well as a potentially unlimited downside.
Take the care of a speculator who buys a two-month Nifty futures contract when the Nifty stands
at 2220. The underlying asset in this case is the Nifty portfolio. When the index moves up, the
long futures position starts making profits, and when the index moves down it starts making
losses.
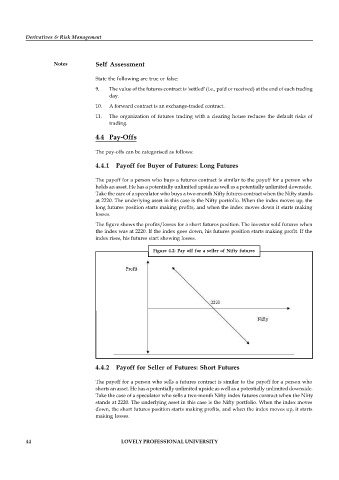
The figure shows the profits/losses for a short futures position. The investor sold futures when
the index was at 2220. If the index goes down, his futures position starts making profit. If the
index rises, his futures start showing losses.
Figure 4.2: Pay off for a seller of Nifty futures
4.4.2 Payoff for Seller of Futures: Short Futures
The payoff for a person who sells a futures contract is similar to the payoff for a person who
shorts an asset. He has a potentially unlimited upside as well as a potentially unlimited downside.
Take the case of a speculator who sells a two-month Nifty index futures contract when the Nifty
stands at 2220. The underlying asset in this case is the Nifty portfolio. When the index moves
down, the short futures position starts making profits, and when the index moves up, it starts
making losses.
44 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY