Page 48 - DMGT513_DERIVATIVES_AND_RISK_MANAGEMENT
P. 48
Unit 4: Future Contracts
Profits and losses of futures contracts are settled everyday at the end of trading, a practice called Notes
'marking the market'. Daily settlements reduce the default risk of futures contracts relative to
forward contracts. On a daily basis, futures investors must pay over any losses or receive any
gains from the day's price movements. An insolvent investor with an unprofitable position
would be forced into default after only one day's trading, rather than being allowed to build up
huge losses that lead to one large default at the time the contract matures (as could occur with a
forward contact).
Futures contracts can also be closed out easily with an 'offsetting trade'. For example, if a
company's long position in $ futures has proved to be profitable, it need not literally take
delivery of the $ at the time the contract matures. Rather, the company can sell futures contracts
on a like amount of $ just prior to the maturity of the long position. The two positions cancel on
the books of the futures exchange and the company receives its profit in cash.
These and other differences between forwards and futures are summarized below in
Table 4.1
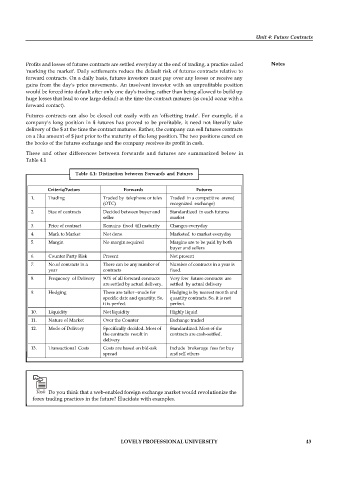
Table 4.1: Distinction between Forwards and Futures
Criteria/Factors Forwards Futures
1. Trading Traded by telephone or telex Traded in a competitive arena(
(OTC) recognized exchange)
2. Size of contracts Decided between buyer and Standardized in each futures
seller market
3. Price of contract Remains fixed till maturity Changes everyday
4. Mark to Market Not done Marketed to market everyday
5. Margin No margin required Margins are to be paid by both
buyer and sellers
6. Counter Party Risk Present Not present
7. No.of contracts in a There can be any number of Number of contracts in a year is
year contracts fixed.
8. Frequency of Delivery 90% of all forward contracts Very few future contracts are
are settled by actual delivery. settled by actual delivery
9. Hedging These are tailor –made for Hedging is by nearest month and
specific date and quantity. So, quantity contracts. So, it is not
it is perfect perfect.
10. Liquidity Not liquidity Highly liquid
11. Nature of Market Over the Counter Exchange traded
12. Mode of Delivery Specifically decided. Most of Standardized. Most of the
the contracts result in contracts are cash-settled.
delivery
13. Transactional Costs Costs are based on bid-ask Include brokerage fees for buy
spread and sell others
Task Do you think that a web-enabled foreign exchange market would revolutionize the
forex trading practices in the future? Elucidate with examples.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 43