Page 178 - DMGT514_MANAGEMENT_CONTROL_SYSTEMS
P. 178
Unit 8: Management Control through Variance Analysis
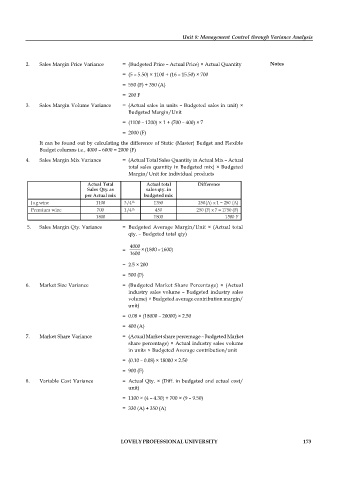
2. Sales Margin Price Variance = (Budgeted Price – Actual Price) × Actual Quantity Notes
= (5 – 5.50) × 1100 + (16 – 15.50) × 700
= 550 (F) + 350 (A)
= 200 F
3. Sales Margin Volume Variance = (Actual sales in units – Budgeted sales in unit) ×
Budgeted Margin/Unit
= (1100 – 1200) × 1 + (700 – 400) × 7
= 2000 (F)
It can be found out by calculating the difference of Static (Master) Budget and Flexible
Budget columns i.e., 4000 – 6000 = 2000 (F)
4. Sales Margin Mix Variance = (Actual Total Sales Quantity in Actual Mix – Actual
total sales quantity in Budgeted mix) × Budgeted
Margin/Unit for individual products
Actual Total Actual total Difference
Sales Qty. as sales qty. in
per Actual mix budgeted mix
th
Jug wine 1100 3/4 1350 250(A) x 1 = 250 (A)
th
Premium wine 700 1/4 450 250 (F) x 7 = 1750 (F)
1800 1800 1500 F
5. Sales Margin Qty. Variance = Budgeted Average Margin/Unit × (Actual total
qty. – Budgeted total qty)
4000
= × (1800 – 1600)
1600
= 2.5 × 200
= 500 (F)
6. Market Size Variance = (Budgeted Market Share Percentage) × (Actual
industry sales volume – Budgeted industry sales
volume) × Budgeted average contribution margin/
unit)
= 0.08 × (18000 – 20000) × 2.50
= 400 (A)
7. Market Share Variance = (Actual Market share percentage – Budgeted Market
share percentage) × Actual industry sales volume
in units × Budgeted Average contribution/unit
= (0.10 – 0.08) × 18000 × 2.50
= 900 (F)
8. Variable Cost Variance = Actual Qty. × (Diff. in budgeted and actual cost/
unit)
= 1100 × (4 – 4.30) + 700 × (9 – 9.50)
= 330 (A) + 350 (A)
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 173