Page 182 - DMGT514_MANAGEMENT_CONTROL_SYSTEMS
P. 182
Unit 8: Management Control through Variance Analysis
Illustration Notes
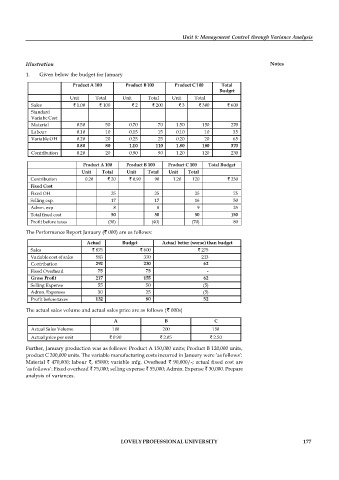
1. Given below the budget for January
Product A 100 Product B 100 Product C 100 Total
Budget
Unit Total Unit Total Unit Total
Sales ` 1.00 ` 100 ` 2 ` 200 ` 3 ` 300 ` 600
Standard
Variabe Cost
Material 0.50 50 0.70 70 1.50 150 270
Labour 0.10 10 0.15 15 0.10 10 35
Variable OH 0.20 20 0.25 25 0.20 20 65
0.80 80 1.10 110 1.80 180 370
Contribution 0.20 20 0.90 90 1.20 120 230
Product A 100 Product B 100 Product C 100 Total Budget
Unit Total Unit Total Unit Total
Contribution 0.20 ` 20 ` 0.90 90 1.20 120 ` 230
Fixed Cost
Fixed OH 25 25 25 75
Selling exp. 17 17 16 50
Admn. exp 8 8 9 25
Total fixed cost 50 50 50 150
Profit before taxes (30) (40) (70) 80
The Performance Report January (` 000) are as follows:
Actual Budget Actual better (worse) than budget
Sales ` 875 ` 600 ` 275
Variable cost of sales 583 370 213
Contribution 292 230 62
Fixed Overhead 75 75 -
Gross Profit 217 155 62
Selling Expense 55 50 (5)
Admn. Expenses 30 25 (5)
Profit before taxes 132 80 52
The actual sales volume and actual sales price are as follows (` 000s)
A B C
Actual Sales Volume 100 200 150
Actual price per unit ` 0.90 ` 2.05 ` 2.50
Further, January production was as follows: Product A 150,000 units; Product B 120,000 units,
product C 200,000 units. The variable manufacturing costs incurred in January were ‘as follows’:
Material ` 470,000; labour `, 65000; variable mfg. Overhead ` 90,000/-; actual fixed cost are
‘as follows’: Fixed overhead ` 75,000; selling expense ` 55,000; Admin. Expense ` 30,000. Prepare
analysis of variances.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 177