Page 186 - DMGT514_MANAGEMENT_CONTROL_SYSTEMS
P. 186
Unit 8: Management Control through Variance Analysis
Notes
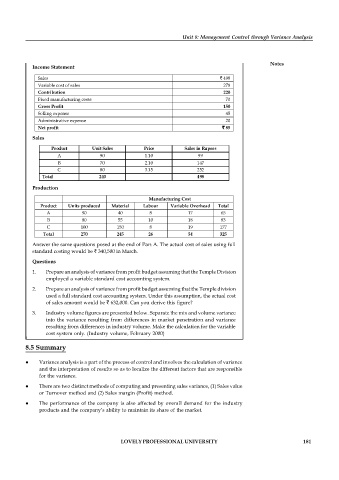
Income Statement
Sales ` 498
Variable cost of sales 278
Contribution 220
Fixed manufacturing costs 70
Gross Profit 150
Selling expense 45
Administrative expense 20
Net profit ` 85
Sales
Product Unit Sales Price Sales in Rupees
A 90 1.10 99
B 70 2.10 147
C 80 3.15 252
Total 240 498
Production
Manufacturing Cost
Product Units produced Material Labour Variable Overhead Total
A 90 40 8 17 65
B 80 55 10 18 83
C 100 150 8 19 177
Total 270 245 26 54 325
Answer the same questions posed at the end of Part A. The actual cost of sales using full
standard costing would be ` 340,500 in March.
Questions
1. Prepare an analysis of variance from profit budget assuming that the Temple Division
employed a variable standard cost accounting system.
2. Prepare an analysis of variance from profit budget assuming that the Temple division
used a full standard cost accounting system. Under this assumption, the actual cost
of sales amount would be ` 632,000. Can you derive this figure?
3. Industry volume figures are presented below. Separate the mix and volume variance
into the variance resulting from differences in market penetration and variance
resulting from differences in industry volume. Make the calculation for the variable
cost system only. (Industry volume, February 2000)
8.5 Summary
Variance analysis is a part of the process of control and involves the calculation of variance
and the interpretation of results so as to localize the different factors that are responsible
for the variance.
There are two distinct methods of computing and presenting sales variance, (1) Sales value
or Turnover method and (2) Sales margin (Profit) method.
The performance of the company is also affected by overall demand for the industry
products and the company’s ability to maintain its share of the market.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 181