Page 266 - DMGT514_MANAGEMENT_CONTROL_SYSTEMS
P. 266
Unit 14: Management Control of MNC’s
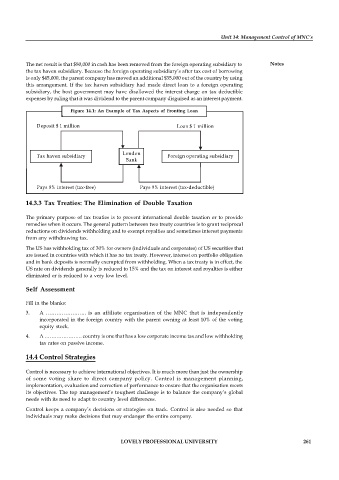
The net result is that $80,000 in cash has been removed from the foreign operating subsidiary to Notes
the tax haven subsidiary. Because the foreign operating subsidiary’s after tax cost of borrowing
is only $45,000, the parent company has moved an additional $35,000 out of the country by using
this arrangement. If the tax haven subsidiary had made direct loan to a foreign operating
subsidiary, the host government may have disallowed the interest charge on tax deductible
expenses by ruling that it was dividend to the parent company disguised as an interest payment.
Figure 14.1: An Example of Tax Aspects of Fronting Loan
Deposit $ 1 million Loan $ 1 million
Tax haven subsidiary London Foreign operating subsidiary
Bank
Pays 8% interest (tax-free) Pays 9% interest (tax-deductible)
14.3.3 Tax Treaties: The Elimination of Double Taxation
The primary purpose of tax treaties is to prevent international double taxation or to provide
remedies when it occurs. The general pattern between two treaty countries is to grant reciprocal
reductions on dividends withholding and to exempt royalties and sometimes interest payments
from any withdrawing tax.
The US has withholding tax of 30% for owners (individuals and corporates) of US securities that
are issued in countries with which it has no tax treaty. However, interest on portfolio obligation
and in bank deposits is normally exempted from withholding. When a tax treaty is in effect, the
US rate on dividends generally is reduced to 15% and the tax on interest and royalties is either
eliminated or is reduced to a very low level.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
3. A ………………….. is an affiliate organisation of the MNC that is independently
incorporated in the foreign country with the parent owning at least 10% of the voting
equity stock.
4. A …………………. country is one that has a low corporate income tax and low withholding
tax rates on passive income.
14.4 Control Strategies
Control is necessary to achieve international objectives. It is much more than just the ownership
of some voting share to direct company policy. Control is management planning,
implementation, evaluation and correction of performance to ensure that the organisation meets
its objectives. The top management’s toughest challenge is to balance the company’s global
needs with its need to adapt to country level differences.
Control keeps a company’s decisions or strategies on track. Control is also needed so that
individuals may make decisions that may endanger the entire company.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 261