Page 270 - DMGT514_MANAGEMENT_CONTROL_SYSTEMS
P. 270
Unit 14: Management Control of MNC’s
European MNEs such as Nestle, than to US MNEs which tend to be dominated by the strong Notes
domestic market. This structure is useful when maximum economies in production can be
gained on a regional rather than on global basis because of market size or the production
technologies for the industry. The drawback is possibly the costly duplication of work among
areas.
Matrix Division Structure
In this structure, a subsidiary reports to more than one group (functional, product or
geographical). The structure is based on the concept that because each group shares responsibility
over foreign operation, the group will become more interdependent, exchange information and
exchange resource, with each other.
Example: Product group managers must compete among themselves to ensure that R&D
personnel responsible to a functional group such as: production, develop technologies for their
product groups.
These product group managers also must compete to ensure that geographic group managers
emphasise their lines sufficiently. Not only product group but also functional and geographic
groups must compete among themselves to obtain resources held by others in the matter. The
matrix organisation has drawbacks that groups compete for scarce resources and how they enact
their preferred operating methods.
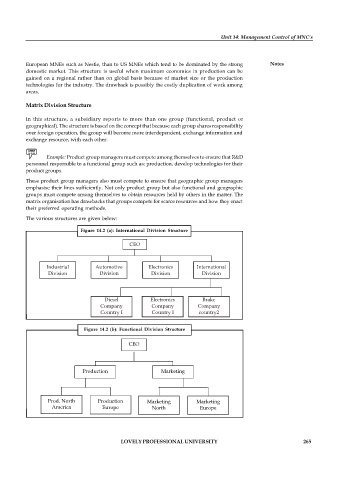
The various structures are given below:
Figure 14.2 (a): International Division Structure
CEO
Industrial Automotive Electronics International
Division Division Division Division
Diesel Electronics Brake
Company Company Company
Country I Country I country2
Figure 14.2 (b): Functional Division Structure
CEO
Production Marketing
Prod. North Production Marketing Marketing
America Europe North Europe
America
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 265