Page 116 - DMGT519_Conflict Management and Negotiation Skills
P. 116
Source of Power
Description
Informational
Information: The accumulation and presentation of
data intended to change the other person’s point of
view or position on an issue.
An
Expertise:
information, or mastery of a body of information, on a
particular problem or issue.
Expertise power can be positive (we believe the other
because of their acknowledged expertise) or negative
(we so distrust the other that their claimed expertise
leads us to pursue a course of action opposite to the
one they advocate). acknowledged accumulation of
Personality and Power derived from differences in
individual differences Psychological orientation (broad orientations to power
use).
Cognitive orientation (ideologies about power).
Conflict Management and Negotiation Skills Motivational orientation (specific motives to use power).
Dispositions and skills (orientations to
cooperation/competition).
Moral orientation (philosophical orientations to power
use).
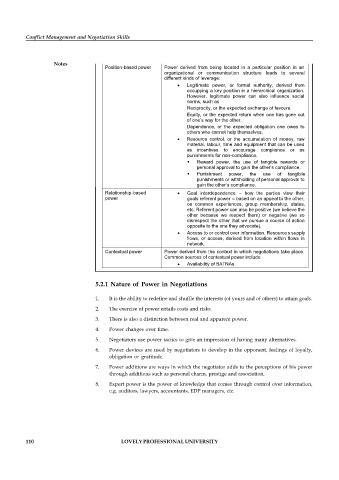
Notes
Position-based power Power derived from being located in a particular position in an
organizational or communication structure leads to several
different kinds of leverage:
Legitimate power, or formal authority, derived from
occupying a key position in a hierarchical organization.
However, legitimate power can also influence social
norms, such as
Reciprocity, or the expected exchange of favours.
Equity, or the expected return when one has gone out
of one’s way for the other.
Dependence, or the expected obligation one owes to
others who cannot help themselves.
Resource control, or the accumulation of money, raw
material, labour, time and equipment that can be used
as incentives to encourage compliance or as
punishments for non-compliance.
Reward power, the use of tangible rewards or
personal approval to gain the other’s compliance.
Punishment power, the use of tangible
punishments or withholding of personal approval to
gain the other’s compliance.
Relationship-based Goal interdependence – how the parties view their
power goals referent power – based on an appeal to the other,
on common experiences, group membershi p, status,
etc. Referent power can also be positive (we believe the
other because we respect them) or negative (we so
disrespect the other that we pursue a course of action
opposite to the one they advocate).
Access to or control over information. Resource s supply
flows, or access, derived from location within flows in
network.
Contextual power Power derived from the context in which negotiations take place.
Common sources of contextual power include
Availability of BATNAs.
5.2.1 Nature of Power in Negotiations
1. It is the ability to redefine and shuffle the interests (of yours and of others) to attain goals.
2. The exercise of power entails costs and risks.
3. There is also a distinction between real and apparent power.
4. Power changes over time.
5. Negotiators use power tactics to give an impression of having many alternatives.
6. Power devices are used by negotiators to develop in the opponent, feelings of loyalty,
obligation or gratitude.
7. Power additions are ways in which the negotiator adds to the perceptions of his power
through additions such as personal charm, prestige and association.
8. Expert power is the power of knowledge that comes through control over information,
e.g. auditors, lawyers, accountants, EDP managers, etc.
110 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY