Page 258 - DMGT519_Conflict Management and Negotiation Skills
P. 258
Conflict Management and Negotiation Skills
Notes 12.6 Applying Ethical Reasoning to Negotiation
For instance, in a situation involving selling a stereo and the statement to a prospective buyer
about the existence of another potential buyer:
1. If you believed in end-result ethics, then you might do whatever was necessary to get the
best possible outcome (including telling lie about an alternative buyer).
2. If you believed in duty ethics, you might perceive an obligation never to engage in
subterfuge, and might, therefore, reject a tactic that involves an outright lie.
3. If you believed in social contract ethics you would base your tactical choices on your view
of appropriate conduct for behaviour in your community; if others would use deception
in a situation like this, you lie.
4. If you believed in personalistic ethics, you would consult your conscience and decide
whether your need for cash for your upcoming trip justified using deceptive or dishonest
tactics.
12.7 Ethics versus Prudence versus Practicality versus Legality
Discussions of business ethics frequently confuse what is ethical (appropriate as determined by
some standard of moral conduct) versus what is prudent (wise, based on trying to understand
the efficacy of the tactic and the consequences it might have on the relationship with the other)
versus what is practical (what a negotiator can actually make happen in a given situation?)
versus what is legal (what the law defines as acceptable practice?) (Missner, 1980).
Each of these approach could be used to analyse the four hypothetical standards mentioned at
the beginning of the unit:
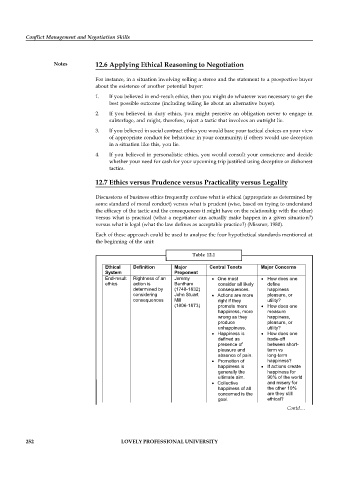
Table 12.1
Ethical Definition Major Central Tenets Major Concerns
System Proponent
End-result Rightness of an Jeremy One must How does one
ethics action is Bentham consider all likely define
determined by (1748-1832) consequences. happiness
considering John Stuart Actions are more pleasure, or
consequences Mill right if they utility?
(1806-1873) promote more How does one
happiness, more measure
wrong as they happiness,
produce pleasure, or
unhappiness. utility?
Happiness is How does one
defined as trade-off
presence of between short-
pleasure and term vs
absence of pain. long-term
Promotion of happiness?
happiness is If actions create
generally the happiness for
ultimate aim. 90% of the world
Collective and misery for
happiness of all the other 10%
concerned is the are they still
goal. ethical?
Human conduct By what
Contd....
should be guided authority do we
by primary moral accept particular
principle. rules or the
Individuals should “goodness” of
stand on their those rules?
principles and Which rule do
252 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY restrain we follow when
themselves by rules conflict?
rules. How do we
The ultimate good adapt general
is a life of virtue rules to fit
(action on specific
principles) rather situations?
than pleasure. How do rules
We should not change as
adjust moral law circumstances
to fit our actions, change?
but adjust our What happens
actions to fit when good rules
moral law. produce bad
consequences?
Are these rules
without any
exceptions?
Social Rightness of Jean-Jacques People must How do we
contract an action is Rousseau function in a determine the
ethics deter- mined (1712-1778) social community general will?
by the context to What is meant
customs and survive. by the “common
norms of a Communities good”?
community become “moral What do we do
bodies” for with
determining independent
ground rules. thinkers who
challenge the