Page 257 - DMGT523_LOGISTICS_AND_SUPPLY_CHAIN_MANAGEMENT
P. 257
Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Notes
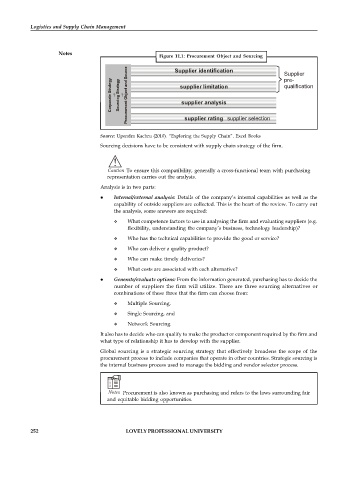
Figure 11.1: Procurement Object and Sourcing
Supplier identification
Supplier
pre-
supplier limitation qualification
supplier analysis
supplier rating supplier selection
Source: Upendra Kachru (2010). “Exploring the Supply Chain”. Excel Books
Sourcing decisions have to be consistent with supply chain strategy of the firm.
!
Caution To ensure this compatibility, generally a cross-functional team with purchasing
representation carries out the analysis.
Analysis is in two parts:
Internal/external analysis: Details of the company’s internal capabilities as well as the
capability of outside suppliers are collected. This is the heart of the review. To carry out
the analysis, some answers are required:
What competence factors to use in analysing the firm and evaluating suppliers (e.g.
flexibility, understanding the company’s business, technology leadership)?
Who has the technical capabilities to provide the good or service?
Who can deliver a quality product?
Who can make timely deliveries?
What costs are associated with each alternative?
Generate/evaluate options: From the information generated, purchasing has to decide the
number of suppliers the firm will utilize. There are three sourcing alternatives or
combinations of these three that the firm can choose from:
Multiple Sourcing,
Single Sourcing, and
Network Sourcing.
It also has to decide who can qualify to make the product or component required by the firm and
what type of relationship it has to develop with the supplier.
Global sourcing is a strategic sourcing strategy that effectively broadens the scope of the
procurement process to include companies that operate in other countries. Strategic sourcing is
the internal business process used to manage the bidding and vendor selector process.
Notes Procurement is also known as purchasing and refers to the laws surrounding fair
and equitable bidding opportunities.
252 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY