Page 82 - DMGT524_TOTAL_QUALITY_MANAGEMENT
P. 82
Unit 6: Customer Retention
Notes
Caselet Rockbridge: A New Paradigm for Understanding
Customer Retention
common paradigm that has emerged from the TQM movement is that the ultimate
path to retaining customers is to satisfy their needs. The theory holds that by
Aidentifying what customers expect, and then meeting and exceeding these
expectations, customers will be far less likely to seek the services of competitors. Over the
past few years, analyses of different satisfaction data bases have validated this theory.
Customer satisfaction is indeed a strong correlate of retention and loyalty. However, the
level of satisfaction with a service does not completely explain loyalty. In one study of a
mass market service, it is discovered that when all the effects of satisfaction were controlled,
the strongest predictor of brand loyalty became the number of years the customer had
used their current brand.
The analysis suggested a new hypothesis about customer retention: some customers will
not change their brand of service even if they are dissatisfied, while others will switch or
try new alternatives even when they are completely satisfied. Other more comprehensive
analyses of the determinants of loyalty and retention have suggested several factors,
beyond satisfaction, that drive retention. These include:
Past behavior
Attitudes about purchasing, such as openness to new services
Perceptions about the loss or gain of switching brands
Demographics
In some cases, a company’s high customer attrition rate may have as much to do with the
type of customer as with the quality of service. Such companies may rely heavily on
aggressive marketing. Customers who are responsive to solicitation are also more likely
to be brand switchers.
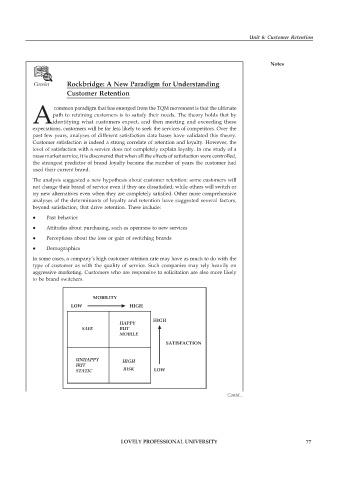
MOBILITY
LOW HIGH
HIGH
HAPPY
SAFE BUT
MOBILE
SATISFACTION
UNHAPPY HIGH
BUT
STATIC RISK LOW
Contd...
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 77