Page 154 - DMGT547_INTERNATIONAL_MARKETING
P. 154
Unit 8: Pricing Decisions for International Markets
Notes
Example: Lockheed (back when it was an independent firm) took Spanish wine in return
for aircraft, and sellers to Eastern Europe have taken their payment in ham.
An offset contract is somewhat more flexible in that the buyer can get paid but instead has to
buy, or cause others to buy, products for a certain value within a specified period of time.
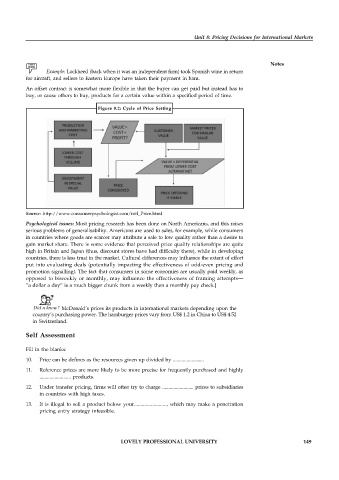
Figure 8.2: Cycle of Price Setting
Source: http://www.consumerpsychologist.com/intl_Price.html
Psychological issues: Most pricing research has been done on North Americans, and this raises
serious problems of generalisability. Americans are used to sales, for example, while consumers
in countries where goods are scarcer may attribute a sale to low quality rather than a desire to
gain market share. There is some evidence that perceived price quality relationships are quite
high in Britain and Japan (thus, discount stores have had difficulty there), while in developing
countries, there is less trust in the market. Cultural differences may influence the extent of effort
put into evaluating deals (potentially impacting the effectiveness of odd-even pricing and
promotion signalling). The fact that consumers in some economies are usually paid weekly, as
opposed to biweekly or monthly, may influence the effectiveness of framing attempts—
”a dollar a day” is a much bigger chunk from a weekly than a monthly pay check.]
Did u know? McDonald’s prices its products in international markets depending upon the
country’s purchasing power. The hamburger prices vary from US$ 1.2 in China to US$ 4.52
in Switzerland.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
10. Price can be defines as the resources given up divided by .........................
11. Reference prices are more likely to be more precise for frequently purchased and highly
......................... products.
12. Under transfer pricing, firms will often try to charge ......................... prices to subsidiaries
in countries with high taxes.
13. It is illegal to sell a product below your........................., which may make a penetration
pricing entry strategy infeasible.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 149