Page 213 - DMGT548_GLOBAL_HRM
P. 213
Global HRM
Notes organisational context. Therefore, the five major constraints identified in multinational
strategy for goal setting for the subsidiary are important considerations strategy
performance management. The type of operation to which the expatriate is assigned is
important.
Example: In China, it is relatively easier to perform in a wholly-owned subsidiary than
in a joint venture with a state-owned enterprise. An expatriate IJV manager may have difficulty
trying to serve two masters and experience a high level of uncertainty regarding the effect of
differing goal expectations for the new IJV upon his performance evaluation.
The stage of the international business will influence the success of the expatriate. An
expatriate overseeing the establishment of a new facility in a foreign country, especially
in a developing or emerging market, will face different challenges and constraints than
one who is posted in a mature operation.
5. Cultural Adjustment: The process of cultural adjustment is a critical determinant of
expatriate job performance. Expatriates and their families will have some difficulty
adjusting to a new environment, and this will impact on the manager’s work performance.
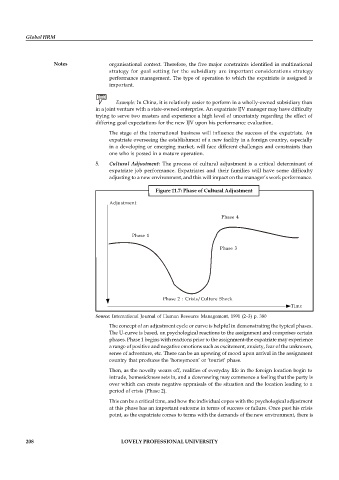
Figure 11.7: Phase of Cultural Adjustment
Adjustment
Phase 4
Phase 1
Phase 3
Phase 2 : Crisis/Culture Shock
Time
Source: International Journal of Human Resource Management, 1991 (2–3) p. 380
The concept of an adjustment cycle or curve is helpful in demonstrating the typical phases.
The U-curve is based, on psychological reactions to the assignment and comprises certain
phases. Phase 1 begins with reactions prior to the assignment-the expatriate may experience
a range of positive and negative emotions such as excitement, anxiety, fear of the unknown,
sense of adventure, etc. There can be an upswing of mood upon arrival in the assignment
country that produces the ‘honeymoon’ or ‘tourist’ phase.
Then, as the novelty wears off, realities of everyday life in the foreign location begin to
intrude, homesickness sets in, and a downswing may commence a feeling that the party is
over which can create negative appraisals of the situation and the location leading to a
period of crisis (Phase 2).
This can be a critical time, and how the individual copes with the psychological adjustment
at this phase has an important outcome in terms of success or failure. Once past his crisis
point, as the expatriate comes to terms with the demands of the new environment, there is
208 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY