Page 54 - DMGT548_GLOBAL_HRM
P. 54
Unit 3: Global Status and Control Mechanism in MNCs
As part of the process of accommodating subsidiary concerns through decentralisation, the Notes
MNC strives to adapt its HRM activities to each host-country’s specific requirements; this impacts
the corporate HRM function. There is devolution of responsibility for local employee decisions
to each subsidiary, with corporate HR staff performing a monitoring role, intervening in local
affairs only in extreme circumstances.
Example: In the late-1980s, Ford Australia had a ceiling on its HRM decisions and any
decision that involved an amount above that ceiling (such as promotions above a certain salary
grade) had to be referred to its regional Headquarters for corporate approval. Expatriate
management remained the responsibility of corporate HR staff.
This HRM monitoring role reflects management’s desire for central control of strategic planning–
formulating, implementing, and coordinating strategies for its worldwide markets. The growth
in foreign exposure combined with changes in the organisational structure of international
operations results in an increase in the number of employees needed to oversee the activities
between the parent firm and its foreign affiliates.
Task Taking the example of any Indian firm, analyse the path which it will follow to
become truly global with the changes in the structure and the HR policies.
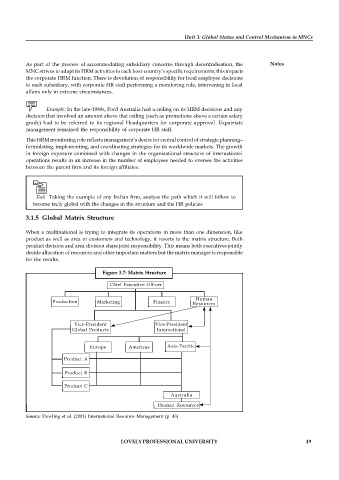
3.1.5 Global Matrix Structure
When a multinational is trying to integrate its operations in more than one dimension, like
product as well as area or customers and technology, it resorts to the matrix structure. Both
product division and area division share joint responsibility. This means both executives jointly
decide allocation of resources and other important matters but the matrix manager is responsible
for the results.
Figure 3.7: Matrix Structure
Chief Executive Officer
Human
Production Marketing Finance Resources
Vice-President Vice-President
Global Products International
Europe Americas Asia-Pacific
Product A
Product B
Product C
Australia
Human Resources
Source: Dowling et al. (2001) International Resource Management (p. 43)
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 49