Page 60 - DMGT548_GLOBAL_HRM
P. 60
Unit 3: Global Status and Control Mechanism in MNCs
The level of strategic control needed in an international operation is depicted along three axes: Notes
the type of subsidiary operating in each country; the type of international business strategy
employed; and the type of ownership.
Perlmutter’s Model
Perlmutter suggested different internationalising strategies that organisations tend to fit which
influence personnel practices within the global context. The ethnocentric approach is probably
closest to global organisation where control is tight from the centre with subsidiaries having
little autonomy and where key positions are held by home-country nations and there is a high
degree of management by expatriates. The polycentric approach sees each subsidiary as a separate
entity. Although subsidiaries are managed by locals, these same local managers are unlikely to
have a career in the international group or at headquarters. The ideal approach is seen as the
geocentric organisation.
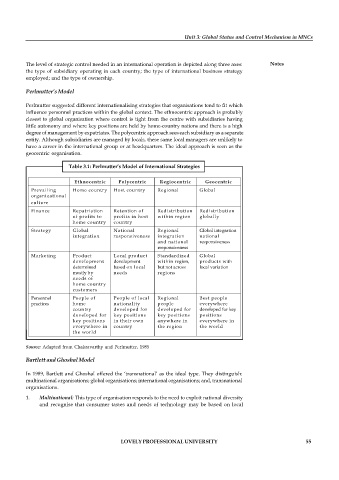
Table 3.1: Perlmutter’s Model of International Strategies
Ethnocentric Polycentric Regiocentric Geocentric
Prevailing Home country Host country Regional Global
organizational
culture
Finance Repatriation Retention of Redistribution Redistribution
of profits to profits in host within region globally
home country country
Strategy Global National Regional Global integration
integration responsiveness integration national
and national responsiveness
responsiveness
Marketing Product Local product Standardized Global
development development within region, products with
determined based on local but not across local variation
mostly by needs regions
needs of
home country
customers
Personnel People of People of local Regional Best people
practices home nationality people everywhere
country developed for developed for developed for key
developed for key positions key positions positions
key positions in their own anywhere in everywhere in
everywhere in country the region the world
the world
Source: Adapted from Chakravarthy and Perlmutter, 1985
Bartlett and Ghoshal Model
In 1989, Bartlett and Ghoshal offered the ‘transnational’ as the ideal type. They distinguish:
multinational organisations; global organisations; international organisations; and, transnational
organisations.
1. Multinational: This type of organisation responds to the need to exploit national diversity
and recognise that consumer tastes and needs of technology may be based on local
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 55