Page 116 - DMGT549_INTERNATIONAL_FINANCIAL_MANAGEMENT
P. 116
Unit 7: Management of Transaction Exposure
High-low Position Index (HLPI) is also shown in Table 7.3. HLPI is an important tool to measure Notes
the volatility of currencies and describes the position of the current exchange rate relative to its
one year high and low. For example, a value of 0 means that the current value of a given foreign
currency measured in local units is the lowest within the past 12 months, whereas 100 indicates
that it is the highest. Table 7.3 shows that only three currencies have witnessed large daily
movements with respect to the Indian rupee. The Japanese Yen has appreciated by 0.57% while
the South African and the Swedish krona have depreciated by – 0.60% and – 0.29% respectively.
The movement for 3 months period shows that out of all the currencies South African rand is the
most volatile currency. This could probably be due to the fact that South Africa exhibits an
unusual combination of sophisticated and a developing economy. The Swiss franc and the
basket of European currencies have also appreciated significantly. The US dollar has moved up
by only 0.25%. An analysis of the one year data reveals that once again the South African rand is
the most volatile and has lost one sixth of its value in the last one year. Apart from this, the
Indian rupee has appreciated with respect to only three currencies – Australian dollar ( – 5.51%),
Japanese yen ( – 8.11%) and Swedish krona ( – 7.19%). With respect to all other currencies it has
depreciated. Overall it can be concluded that the Indian rupee has remained relatively stable in
the last one year with respect to most of the currencies in the world and has moved in only single
digit percentages with respect to all the currencies except the South African rand.
Assigning Risk Grades to Currencies
Risk grades to currencies have been arrived at after determining their standard deviations. The
following formula has been used for arriving at the classification:
Standard Deviation 2000
× 100
Standard Deviation 1991
Here 1991 is our base year for currency fluctuations while 2000 is the most current year. Based on
this data on currency variability’s, we have assigned risk grades as predictive of currency
behaviour.
The grades have been assigned as per the following parameters:
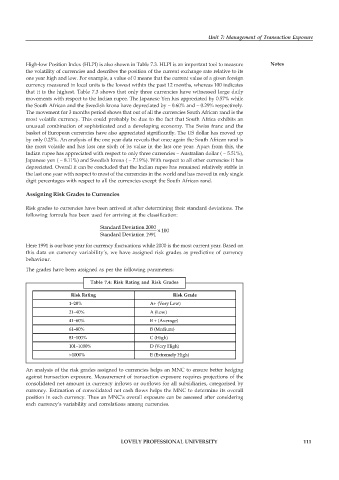
Table 7.4: Risk Rating and Risk Grades
Risk Rating Risk Grade
1–20% A+ (Very Low)
21–40% A (Low)
41–60% B + (Average)
61–80% B (Medium)
81–100% C (High)
101–1000% D (Very High)
>1000% E (Extremely High)
An analysis of the risk grades assigned to currencies helps an MNC to ensure better hedging
against transaction exposure. Measurement of transaction exposure requires projections of the
consolidated net amount in currency inflows or outflows for all subsidiaries, categorised by
currency. Estimation of consolidated net cash flows helps the MNC to determine its overall
position in each currency. Thus an MNC’s overall exposure can be assessed after considering
each currency’s variability and correlations among currencies.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 111