Page 177 - DMGT549_INTERNATIONAL_FINANCIAL_MANAGEMENT
P. 177
International Financial Management
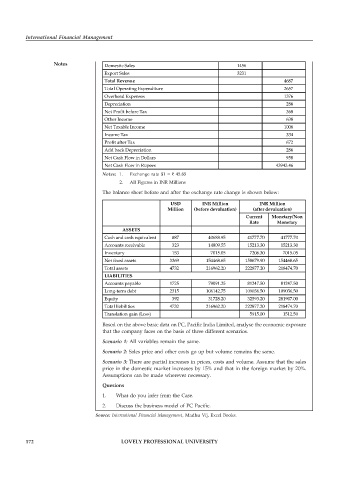
Notes Domestic Sales 1456
Export Sales 3231
Total Revenue 4687
Total Operating Expenditure 2657
Overhead Expenses 1376
Depreciation 286
Net Profit before Tax 368
Other Income 638
Net Taxable Income 1006
Income Tax 334
Profit after Tax 672
Add back Depreciation 286
Net Cash Flow in Dollars 958
Net Cash Flow in Rupees 43943.46
Notes: 1. Exchange rate $1 = ` 45.85
2. All Figures in INR Millions
The balance sheet before and after the exchange rate change is shown below:
USD INR Million INR Million
Million (before devaluation) (after devaluation)
Current Monetary/Non
Rate Monetary
ASSETS
Cash and cash equivalent 887 40688.95 41777.70 41777.70
Accounts receivable 323 14809.55 15213.30 15213.30
Inventory 153 7015.05 7206.30 7015.05
Net fixed assets 3369 154468.65 158679.90 154468.65
Total assets 4732 216962.20 222877.20 218474.70
LIABILITIES
Accounts payable 1725 79091.25 81247.50 81247.50
Long-term debt 2315 106142.75 109036.50 109036.50
Equity 392 31728.20 32593.20 281907.00
Total liabilities 4732 216962.20 222877.20 218474.70
Translation gain (Loss) 5915.00 1512.50
Based on the above basic data on PC, Pacific India Limited, analyse the economic exposure
that the company faces on the basis of three different scenarios.
Scenario 1: All variables remain the same.
Scenario 2: Sales price and other costs go up but volume remains the same.
Scenario 3: There are partial increases in prices, costs and volume. Assume that the sales
price in the domestic market increases by 15% and that in the foreign market by 20%.
Assumptions can be made wherever necessary.
Quesions
1. What do you infer from the Case.
2. Discuss the business model of PC Pacific.
Source: International Financial Management, Madhu Vij, Excel Books.
172 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY