Page 189 - DMGT554_RETAIL_BUYING
P. 189
Retail Buying
Notes which to set its final retail prices. The costs help set the floor, or lower limits, of this range,
whereas the competitors and consumers (product demand) set the upper pricing limits.
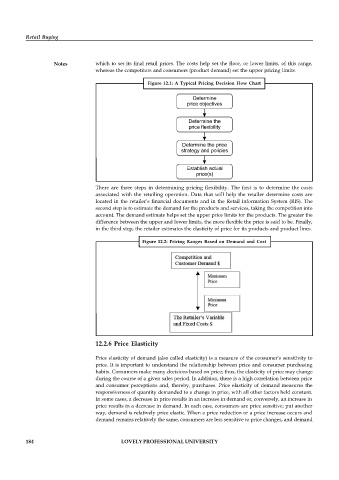
Figure 12.1: A Typical Pricing Decision Flow Chart
There are three steps in determining pricing flexibility. The first is to determine the costs
associated with the retailing operation. Data that will help the retailer determine costs are
located in the retailer’s financial documents and in the Retail Information System (RIS). The
second step is to estimate the demand for the products and services, taking the competition into
account. The demand estimate helps set the upper price limits for the products. The greater the
difference between the upper and lower limits, the more flexible the price is said to be. Finally,
in the third step, the retailer estimates the elasticity of price for its products and product lines.
Figure 12.2: Pricing Ranges Based on Demand and Cost
12.2.6 Price Elasticity
Price elasticity of demand (also called elasticity) is a measure of the consumer’s sensitivity to
price. It is important to understand the relationship between price and consumer purchasing
habits. Consumers make many decisions based on price; thus, the elasticity of price may change
during the course of a given sales period. In addition, there is a high correlation between price
and consumer perceptions and, thereby, purchases. Price elasticity of demand measures the
responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price, with all other factors held constant.
In some cases, a decrease in price results in an increase in demand or, conversely, an increase in
price results in a decrease in demand. In each case, consumers are price sensitive; put another
way, demand is relatively price elastic. When a price reduction or a price increase occurs and
demand remains relatively the same, consumers are less sensitive to price changes, and demand
184 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY