Page 82 - DLIS408_INFORMATION_TECHNOLOGY-APPLICATIONSL SCIENCES
P. 82
Unit 6: Information and Communications Technology
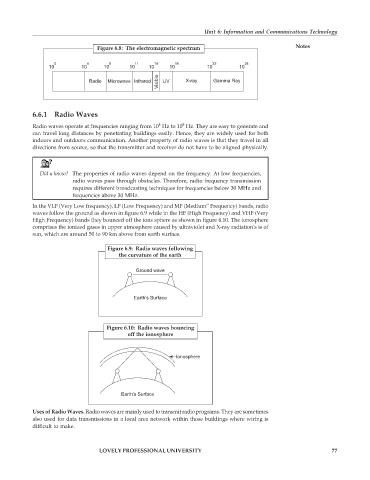
Figure 6.8: The electromagnetic spectrum Notes
0 4 8 11 14 16 22 24
10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
Visible
Radio Microwave Infrared UV X-ray Gamma Ray
6.6.1 Radio Waves
4
8
Radio waves operate at frequencies ranging from 10 Hz to 10 Hz. They are easy to generate and
can travel long distances by penetrating buildings easily. Hence, they are widely used for both
indoors and outdoors communication. Another property of radio waves is that they travel in all
directions from source, so that the transmitter and receiver do not have to be aligned physically.
Did u know? The properties of radio waves depend on the frequency. At low frequencies,
radio waves pass through obstacles. Therefore, radio frequency transmission
requires different broadcasting techniques for frequencies below 30 MHz and
frequencies above 30 MHz.
In the VLF (Very Low frequency), LF (Low Frequency) and MF (Medium” Frequency) bands, radio
waves follow the ground as shown in figure 6.9 while in the HF (High Frequency) and VHF (Very
High Frequency) bands they bounced off the ions sphere as shown in figure 6.10. The ionosphere
comprises the ionized gases in upper atmosphere caused by ultraviolet and X-ray radiation's is of
sun, which are around 50 to 90 km above from earth surface.
Figure 6.9: Radio waves following
the curvature of the earth
Ground wave
Earth’s Surface
Figure 6.10: Radio waves bouncing
off the ionosphere
Ionosphere
Earth’s Surface
Uses of Radio Waves. Radio waves are mainly used to transmit radio programs. They are sometimes
also used for data transmissions in a local area network within those buildings where wiring is
difficult to make.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 77