Page 83 - DLIS408_INFORMATION_TECHNOLOGY-APPLICATIONSL SCIENCES
P. 83
Information Technology and Application
Notes 6.6.2 Microwave Towers
8
The frequencies of microwave portion of the electromagnetic spectrum range from 10 Hz (100
11
MHz) to 10 Hz. Microwaves travels in straight lines and hence, can be narrowly focussed using a
parabolic antenna like a satellite TV dish antenna. In microwave transmission, data is transmitted
between remote locations through microwaves by means of receivers and transmitters placed at
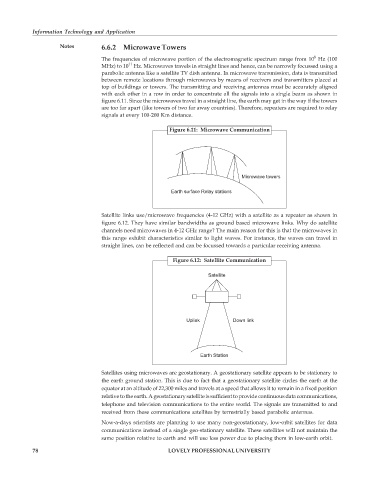
top of buildings or towers. The transmitting and receiving antennas must be accurately aligned
with each other in a row in order to concentrate all the signals into a single beam as shown in
figure 6.11. Since the microwaves travel in a straight line, the earth may get in the way if the towers
are too far apart (like towers of two far away countries). Therefore, repeaters are required to relay
signals at every 100-200 Km distance.
Figure 6.11: Microwave Communication
Microwave towers
Earth surface Relay stations
Satellite links use/microwave frequencies (4-12 GHz) with a satellite as a repeater as shown in
figure 6.12. They have similar bandwidths as ground based microwave links. Why do satellite
channels need microwaves in 4-12 GHz range? The main reason for this is that the microwaves in
this range exhibit characteristics similar to light waves. For instance, the waves can travel in
straight lines, can be reflected and can be focussed towards a particular receiving antenna.
Figure 6.12: Satellite Communication
Satellite
Uplink Down link
Earth Station
Satellites using microwaves are geostationary. A geostationary satellite appears to be stationary to
the earth ground station. This is due to fact that a geostationary satellite circles the earth at the
equator at an altitude of 22,300 miles and travels at a speed that allows it to remain in a fixed position
relative to the earth. A geostationary satellite is sufficient to provide continuous data communications,
telephone and television communications to the entire world. The signals are transmitted to and
received from these communications satellites by terrestrially based parabolic antennas.
Now-a-days scientists are planning to use many non-geostationary, low-orbit satellites for data
communications instead of a single geo-stationary satellite. These satellites will not maintain the
same position relative to earth and will use less power due to placing them in low-earth orbit.
78 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY