Page 63 - DCOM203_DMGT204_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_I
P. 63
Quantitative Techniques – I
Notes 12. Frequency Polygon
13. Frequency Curve
14. 'Ogive' or Cumulative Frequency Curve
1. Line Diagram: In case of a line diagram, different values are represented by the length of
the lines, drawn vertically or horizontally. The gap between the successive lines is kept
uniform. The comparison of values of various items is done by the length of these lines.
Although the comparison is easy, the diagram is not very attractive. This diagram is used
when the number of items is relatively large.
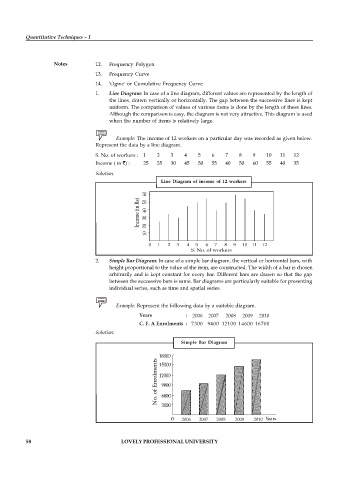
Example: The income of 12 workers on a particular day was recorded as given below.
Represent the data by a line diagram.
S. No. of workers : 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Income ( in ) : 25 35 30 45 50 55 40 50 60 55 40 35
Solution.
Line Diagram of income of 12 workers
2. Simple Bar Diagram: In case of a simple bar diagram, the vertical or horizontal bars, with
height proportional to the value of the item, are constructed. The width of a bar is chosen
arbitrarily and is kept constant for every bar. Different bars are drawn so that the gap
between the successive bars is same. Bar diagrams are particularly suitable for presenting
individual series, such as time and spatial series.
Example: Represent the following data by a suitable diagram.
Years : 2006 2007 2008 009 010
2
2
C. F. A Enrolments : 7300 9400 12100 14600 16700
Solution:
Simple Bar Diagram
2006 2007 2008 2009 2010
58 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY