Page 64 - DCOM203_DMGT204_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_I
P. 64
Unit 4: Presentation of Data
3. Multiple Bar Diagram: This type of diagram, also known as compound bar diagram, is Notes
used when comparisons are to be shown between two or more sets of data. A set of bars for
a period or a related phenomena are drawn side by side without gaps while various sets
of bars are separated by some arbitrarily chosen constant gap. Different bars are
distinguished by different shades or colours. In order that various bars are comparable, it
is necessary to draw them on the same scale.
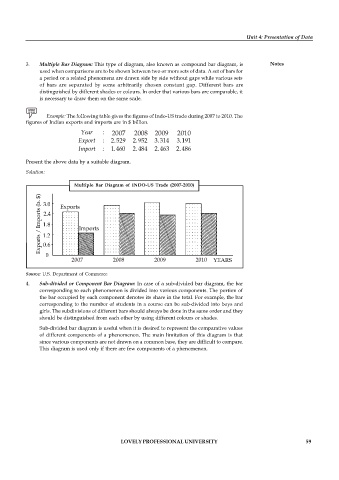
Example: The following table gives the figures of Indo-US trade during 2007 to 2010. The
figures of Indian exports and imports are in $ billion.
Year : 2007 2008 2009 2010
Export : 2.529 2.952 3.314 3.191
Import : 1.460 2.484 2.463 2.486
Present the above data by a suitable diagram.
Solution:
Multiple Bar Diagram of INDO-US Trade (2007-2010)
2007 2008 2009 2010
Source: U.S. Department of Commerce
4. Sub-divided or Component Bar Diagram: In case of a sub-divided bar diagram, the bar
corresponding to each phenomenon is divided into various components. The portion of
the bar occupied by each component denotes its share in the total. For example, the bar
corresponding to the number of students in a course can be sub-divided into boys and
girls. The subdivisions of different bars should always be done in the same order and they
should be distinguished from each other by using different colours or shades.
Sub-divided bar diagram is useful when it is desired to represent the comparative values
of different components of a phenomenon. The main limitation of this diagram is that
since various components are not drawn on a common base, they are difficult to compare.
This diagram is used only if there are few components of a phenomenon.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 59