Page 66 - DCOM203_DMGT204_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_I
P. 66
Unit 4: Presentation of Data
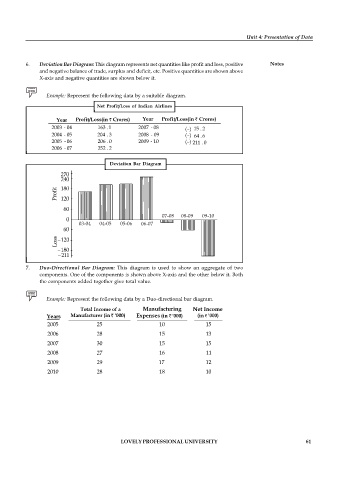
6. Deviation Bar Diagram: This diagram represents net quantities like profit and loss, positive Notes
and negative balance of trade, surplus and deficit, etc. Positive quantities are shown above
X-axis and negative quantities are shown below it.
Example: Represent the following data by a suitable diagram.
Net Profit/Loss of Indian Airlines
Year Profit/Loss(in Crores) Year Profit/Loss(in Crores)
2003 04 163 .1 2007 08 (–) 15 2
-
-
.
2004 05 204 . 3 2008 - 09 (–) 64 6
-
.
2005 06 206 . 0 2009 10 (–) 211 0
-
-
.
-
2006 07 252 . 2
Deviation Bar Diagram
07-08 08-09 09-10
03-04 04-05 05-06 06-07
7. Duo-Directional Bar Diagram: This diagram is used to show an aggregate of two
components. One of the components is shown above X-axis and the other below it. Both
the components added together give total value.
Example: Represent the following data by a Duo-directional bar diagram.
Total Income of a Manufacturing Net Income
Years Manufacturer (in '000) Expenses (in '000) (in '000)
2005 25 10 15
2006 28 15 13
2007 30 15 15
2008 27 16 11
2009 29 17 12
2010 28 18 10
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 61