Page 210 - DCAP402_DCAO204_DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM_MANAGING DATABASE
P. 210
Unit 12: Query Processing and Optimization
Notes
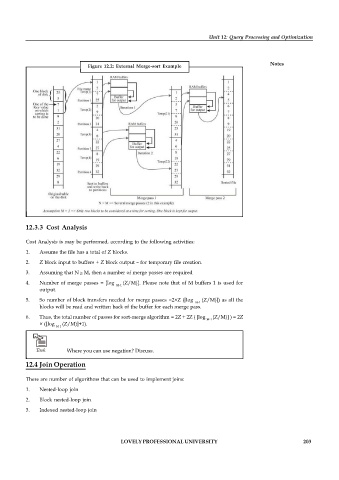
Figure 12.2: External Merge-sort Example
12.3.3 Cost Analysis
Cost Analysis is may be performed, according to the following activities:
1. Assume the file has a total of Z blocks.
2. Z block input to buffers + Z block output – for temporary file creation.
3. Assuming that N M, then a number of merge passes are required
4. Number of merge passes = [log (Z/M)]. Please note that of M buffers 1 is used for
M-1
output.
5. So number of block transfers needed for merge passes =2×Z ([log (Z/M)]) as all the
M-1
blocks will be read and written back of the buffer for each merge pass.
6. Thus, the total number of passes for sort-merge algorithm = 2Z + 2Z ( [log (Z/M)] ) = 2Z
M-1
× ([log (Z/M)]+1).
M-1
Task Where you can use negation? Discuss.
12.4 Join Operation
There are number of algorithms that can be used to implement joins:
1. Nested-loop join
2. Block nested-loop join
3. Indexed nested-loop join
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 203