Page 231 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 231
Microeconomic Theory
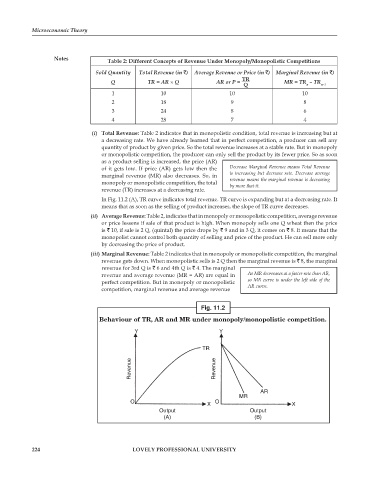
Notes Table 2: Different Concepts of Revenue Under Monopoly/Monopolistic Competitions
Sold Quantity Total Revenue (in ) Average Revenue or Price (in ) Marginal Revenue (in )
TR
___
Q TR = AR × Q AR or P = MR = TR – TR
Q n n–1
1 10 10 10
2 18 9 8
3 24 8 6
4 28 7 4
(i) Total Revenue: Table 2 indicates that in monopolistic condition, total revenue is increasing but at
a decreasing rate. We have already learned that in perfect competition, a producer can sell any
quantity of product by given price. So the total revenue increases at a stable rate. But in monopoly
or monopolistic competition, the producer can only sell the product by its fewer price. So as soon
as a product selling is increased, the price (AR)
of it gets low. If price (AR) gets low then the Decrease Marginal Revenue means Total Revenue
marginal revenue (MR) also decreases. So, in is increasing but decrease rate. Decrease average
monopoly or monopolistic competition, the total revenue means the marginal revenue is decreasing
revenue (TR) increases at a decreasing rate. by more that it.
In Fig. 11.2 (A), TR curve indicates total revenue. TR curve is expanding but at a decreasing rate. It
means that as soon as the selling of product increases, the slope of TR curve decreases.
(ii) Average Revenue: Table 2, indicates that in monopoly or monopolistic competition, average revenue
or price lessens if sale of that product is high. When monopoly sells one Q wheat then the price
is 10, if sale is 2 Q, (quintal) the price drops by 9 and in 3 Q, it comes on 8. It means that the
monopolist cannot control both quantity of selling and price of the product. He can sell more only
by decreasing the price of product.
(iii) Marginal Revenue: Table 2 indicates that in monopoly or monopolistic competition, the marginal
revenue gets down. When monopolistic sells is 2 Q then the marginal revenue is 8, the marginal
revenue for 3rd Q is 6 and 4th Q is 4. The marginal
revenue and average revenue (MR = AR) are equal in As MR decresases at a faster rate than AR,
perfect competition. But in monopoly or monopolistic so MR curve is under the left side of the
competition, marginal revenue and average revenue AR curve.
Fig. 11.2
Behaviour of TR, AR and MR under monopoly/monopolistic competition.
Y Y
TR
Revenue Revenue
AR
MR
O O
X X
Output Output
(A) (B)
224 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY